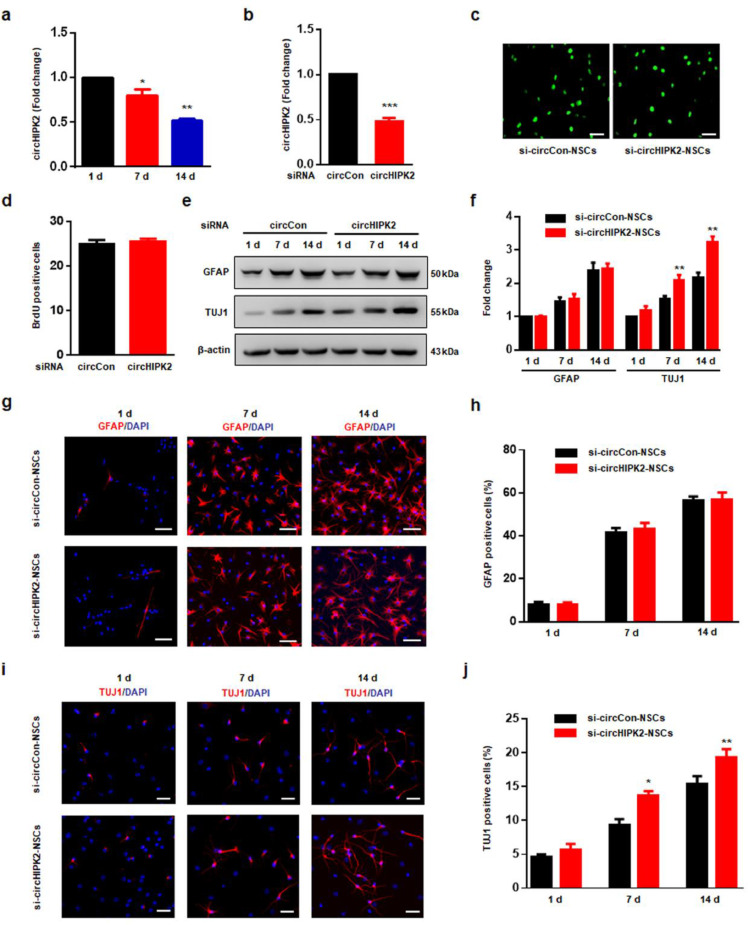
Fig. 1.
circHIPK2 is involved in the differentiation of NSCs. (a) qPCR analysis of circHIPK2 expression in NSCs cultured for 1, 7, and 14 d in differentiation medium. All data were presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs the 1 d one-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc multiple comparison test. (b) qPCR confirmed that circHIPK2 siRNA lentivirus-transducted NSCs successfully decreased circHIPK2 expression. All data were presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 vs the circCon siRNA group using Student's t-test. (c-d) Representative image of BrdU immunostaining (c) and quantification of BrdU immunofluorescence-positive cell numbers (d). All data were presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. (e-f) Western blot analysis showing GFAP (astrocyte marker) and TUJ1 (neuronal marker) protein expression in the si-circCon-NSC group and in the si-circHIPK2-NSC group. All data were presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs the si-circCon-NSCs using two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc multiple comparison test. (g–j) Representative immunostaining of GFAP+ (g) or TUJ1+ (i) cells from differentiated NSCs with si-circHIPK2 lentivirus transduction. Scale bar = 50 μm. Quantification of GFAP+ (h) or TUJ1+ (j) cell numbers using ImageJ software. Timescale indicates days after NSC differentiation. All data were presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs the si-circCon-NSC group cultured in differentiation medium for 7 and 14 d using two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc multiple comparison test.