Figure 7.
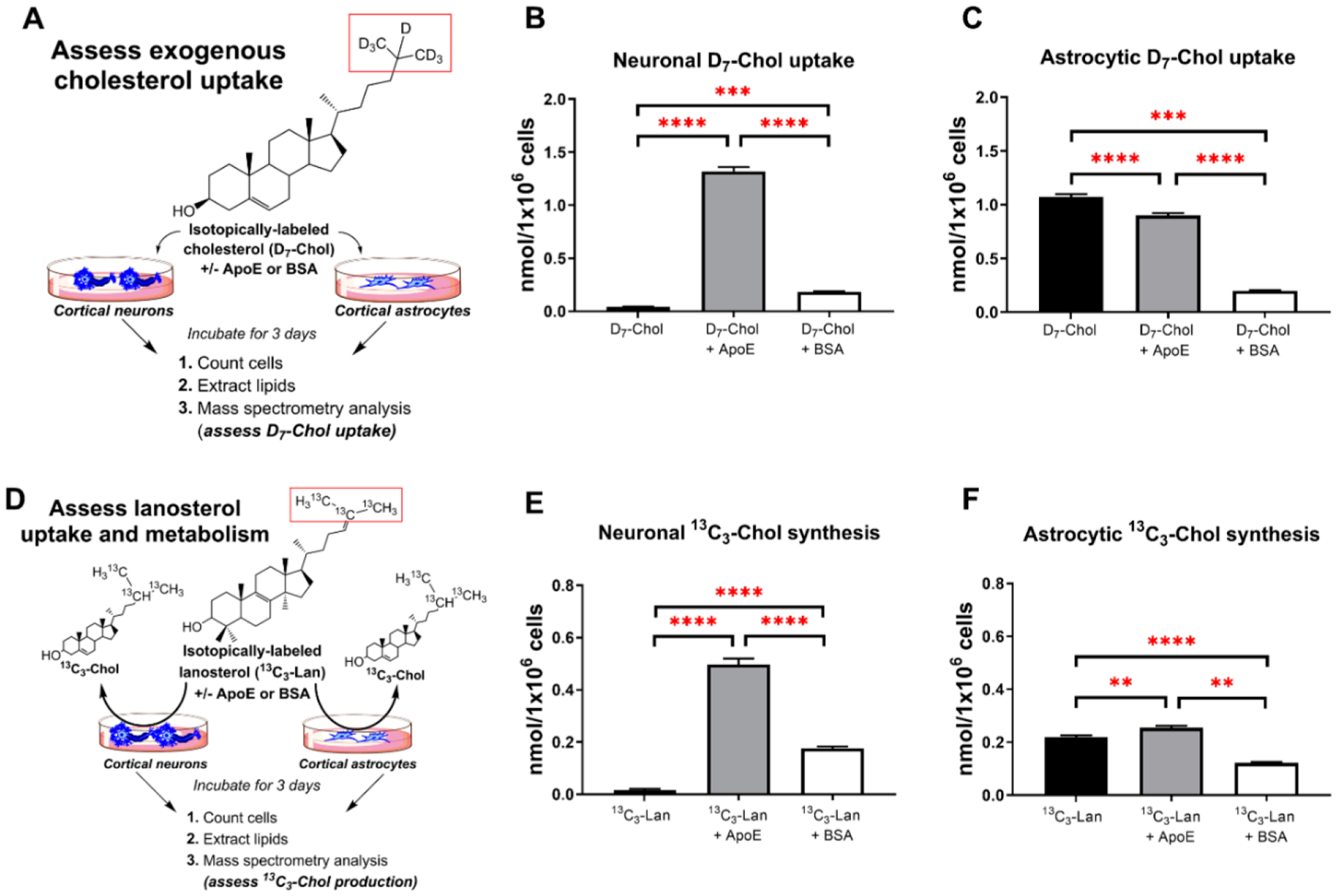
Neuronal and astrocytic uptake of exogenous sterols. Neurons and astrocytes were cultured in defined cholesterol-free medium supplemented with free isotopically labeled cholesterol (D7-Chol), D7-Chol precomplexed with ApoE, and D7-Chol precomplexed with BSA as illustrated in Panel A. The labeled moiety is highlighted in red. Final concentration of D7-Chol in all conditions was 500 nM; protein final concentration was 0.7 μg/mL (either ApoE or BSA). Panels B and C show the uptake of D7-Chol from the medium by neurons and astrocytes, respectively. D7-Chol levels were normalized to the total cell count at the end point of the experiment (DIC3). Sterol values correspond to the mean ± SEM of 8–12 replicates. Note that ApoE facilitates the uptake of D7-Chol by neurons but not by astrocytes. Panel D denotes the experimental design to test the incorporation of 13C3−Lanosterol by neurons and astrocytes. Cells were cultured in defined cholesterol-free medium and with free isotopically labeled lanosterol (13C3−Lan), 13C3−Lan precomplexed with ApoE, and 13C3−Lan precomplexed with BSA. The labeled moiety is highlighted in red. Panels E and F show 13C3−Chol levels derived from the conversion of 13C3−Lan by neurons and astrocytes, respectively. 13C3−Chol levels were normalized to the total cell count at the end point of each experiment. Sterol values correspond to the mean ± SEM of 8–12 replicates. Note that the uptake and conversion of lanosterol into cholesterol is 40-fold higher in neurons when lanosterol is precomplexed with ApoE, while in astrocytes the same treatment increases only by 15%. In all panels, statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001).
