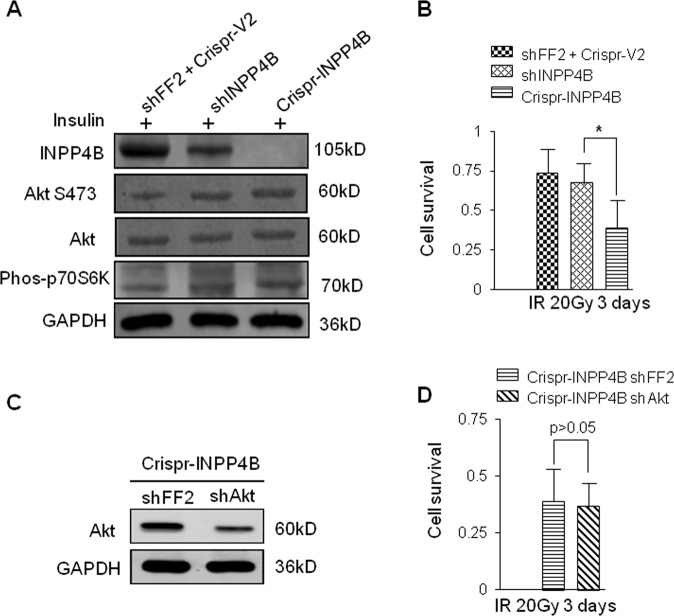
Fig. 3. Activation of Akt is not major cause for IR sensitization in INPP4B knockdown cells.
a A similar level of AKT activation occurred in both INPP4B knockdown and INPP4B knockout cells. Each cell line was serum starved for 72 h, followed by addition of 100 nM insulin for 20 min. Cells were harvested, phosphorylation of Akt, p70S6K and expression of INPP4B were determined by Western blotting, GADPH was served as loading control. b The IR sensitization was only observed in Crispr-INPP4B cells, but not in shINPP4B cells. The three indicated cell lines were seeded into 3.5 cm plates at 3 × 105 /plate. After one day of culture, cells were irradiated with 20 Gy of IR, survival cells were counted on day 3 post IR, the average survival rates were normalized to the untreated cells immediately prior to IR irradiation and plotted in b. *p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference of cell survival between Crispr-INPP4B and shINPP4B cells by one-way ANOVA test. c Knockdown of Akt in Crispr-INPP4B cells was confirmed by Western blot, shFF2 was used as a negative control. d Downregulation of Akt in Crispr-INPP4B A549 cells does not affect their IR sensitivity. The two indicated cell lines were cultured and treated as the same as described in b and cell survival rates were measured on day 3, p > 0.05 by Student’s t test.