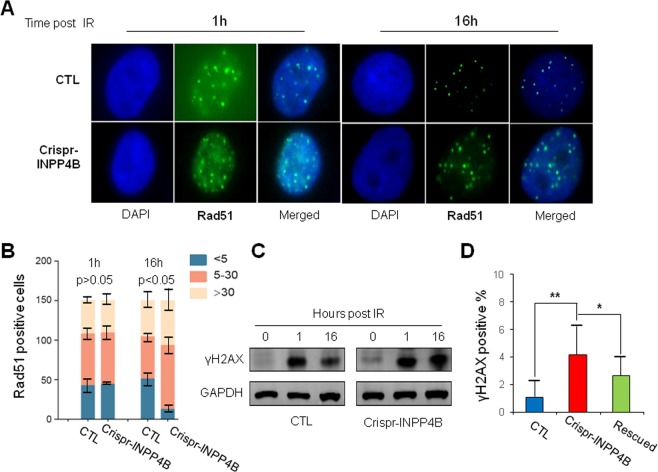
Fig. 4. Prolonged γH2AX activation and Rad51 foci formation in Crispr-INPP4B A549 cells implicate impairment of HR repair.
a The number and signal intensity of Rad51 foci remain high in Crispr-INPP4B A549 cells after 16 h of recovery post 10 Gy IR compared with CTL cells. At the indicated recovery time point, cells were fixed, permeabilized and processed for immunofluorescence staining using antibodies against Rad51. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Representative foci formation images at the indicated time points were shown at a magnification of x1000. b Quantitative summaries of Rad51 foci. The foci numbers were counted in a total of 150 cells at 1 h and 16 h time points post IR by fluorescence microscopy. The cells were divided into 3 sub-groups by foci number: <5 per nucleus, 5–30 per nucleus, and >30 per nucleus. Error bars indicate the standard deviation occurred in each sub-group. Positive cells in 5–30 sub-group were statistically compared between CTL and Crispr-INPP4B cells by Student’s t-test. c Western blotting confirmed the signal of γH2AX was decreased in CTL A549 cells after 16 h of IR recovery while remained high in Crispr-INPP4B A549 cells. d A significant increase of spontaneous endogenous γH2AX foci was observed in the cells with loss of INPP4B expression. A total of 150 cells were observed and counted under fluorescence microscopy. The mean percentage of γH2AX foci positive cells in each cell line was plotted. Asterisk (*) indicates p < 0.05 and asterisks (**) indicates p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA test.