Fig. 3. Proposed mechanism of HSCs oxidative damage and senescence.
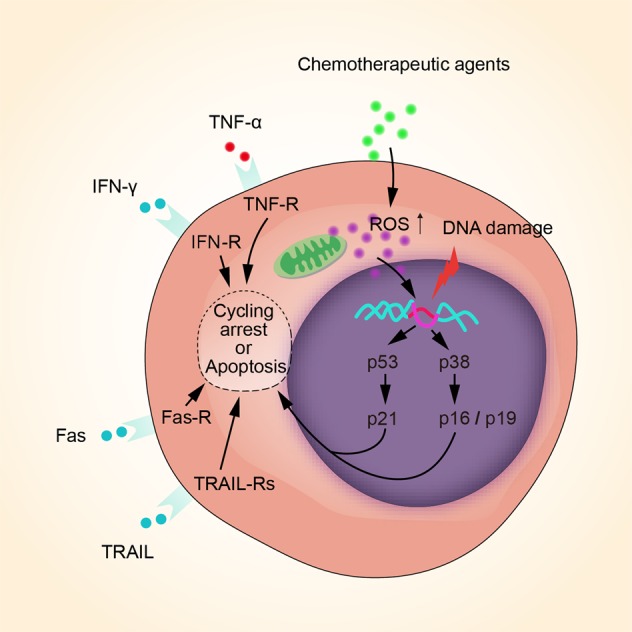
Chemotherapy, especially pro-oxidative chemotherapy, leads to a considerable increase of ROS derived from mitochondria and other resources, inevitably inducing DNA oxidative injury of HSCs. In that case, cell cycle arrest is elicited by p53–p21and p38–p16/19 pathways to repair DNA, whereas cell cycle arrest is the main cause of cell senescence. If DNA injury cannot be repaired, both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways will be activated via various pathways, leading to cell apoptosis. Besides, TNF-α, IFN-γ, Fas, and TRAIL bind to their receptors and lead to HSCs cycle arrest or apoptosis.
