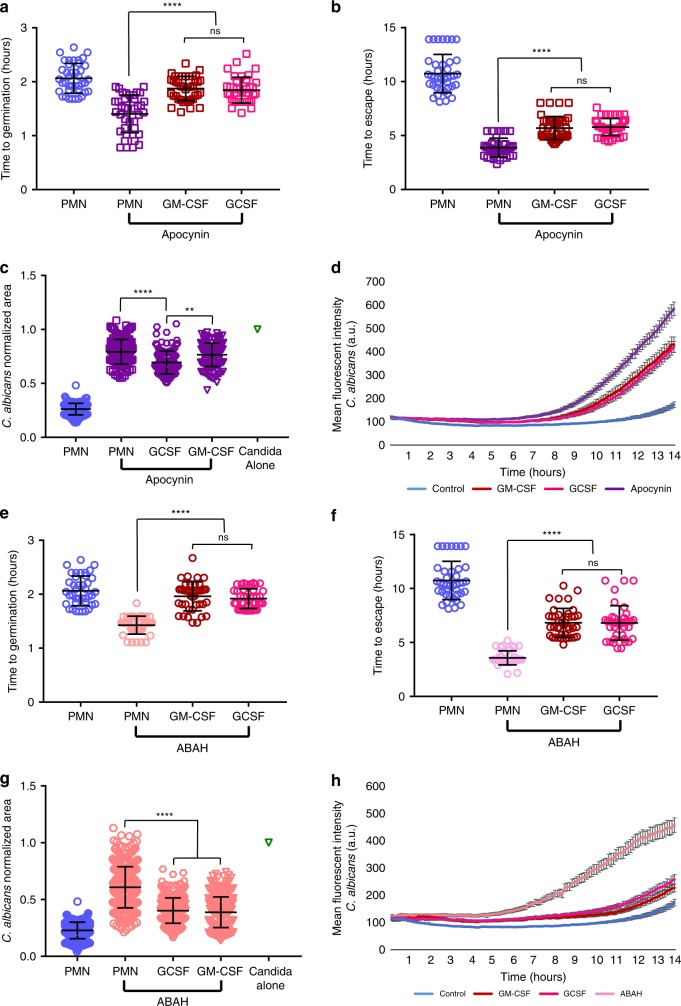
Fig. 7. GM-CSF and GCSF treatment enhance swarming during ROS or MPO inhibition.
GM-CSF or GCSF treatment can partially rescue swarming mediated fungal restriction. Apocynin treatment allows earlier C. albicans germination, while GM-CSF or GSF treatment restores some delay. N = 40 swarms across 3 donors (a). GM-CSF or GCSF treatment partially rescues swarming restriction of hyphal escape. N = 40 swarms across 3 donors (b). GM-CSF or GCSF treatment results in a small reduction in fungal growth at 16 hours. N = 256 swarms for the PMN group, N = 226 swarms for the Apocynin group, N = 210 swarms for the Apocynin+GCSF group, N = 208 swarms for the Apocynin+GM-CSF group, all across 3 independent donors (c). The MFI of C. albicans in swarms treated with Apocynin or both Apocyin and GM-CSF or GCSF was quantified over 14 hours. N = 16 swarms from a representative donor (d). ABAH treatment allows earlier C. albicans germination, while GM-CSF or GSF treatment restores some delay. N = 40 swarms across 3 donors (e). GM-CSF or GCSF treatment partially rescues swarming restriction of hyphal escape. N = 40 swarms across 3 donors (f). GM-CSF or GCSF treatment results in a reduction in fungal growth at 16 hours. N = 341 swarms in the PMN group, N = 355 swarms in the ABAH group, N = 342 swarms in the ABAH+GCSF group and N = 349 swarms in the ABAH+GM-CSF group, all across 3 donors (g). The MFI of C. albicans in swarms treated with ABAH or both ABAH and GM-CSF or GCSF was quantified over 14 hours. N = 16 swarms from a representative donor (h). n.s. is non-significant, **p = 0.0010 (c) and ****p <0.0001 (a, b, c, e, f, g). Kruskal-Wallis with Dunns post-test. Error bars represent mean +/− standard deviation for (a–c, e–g) and mean +/− standard error for (d, h).