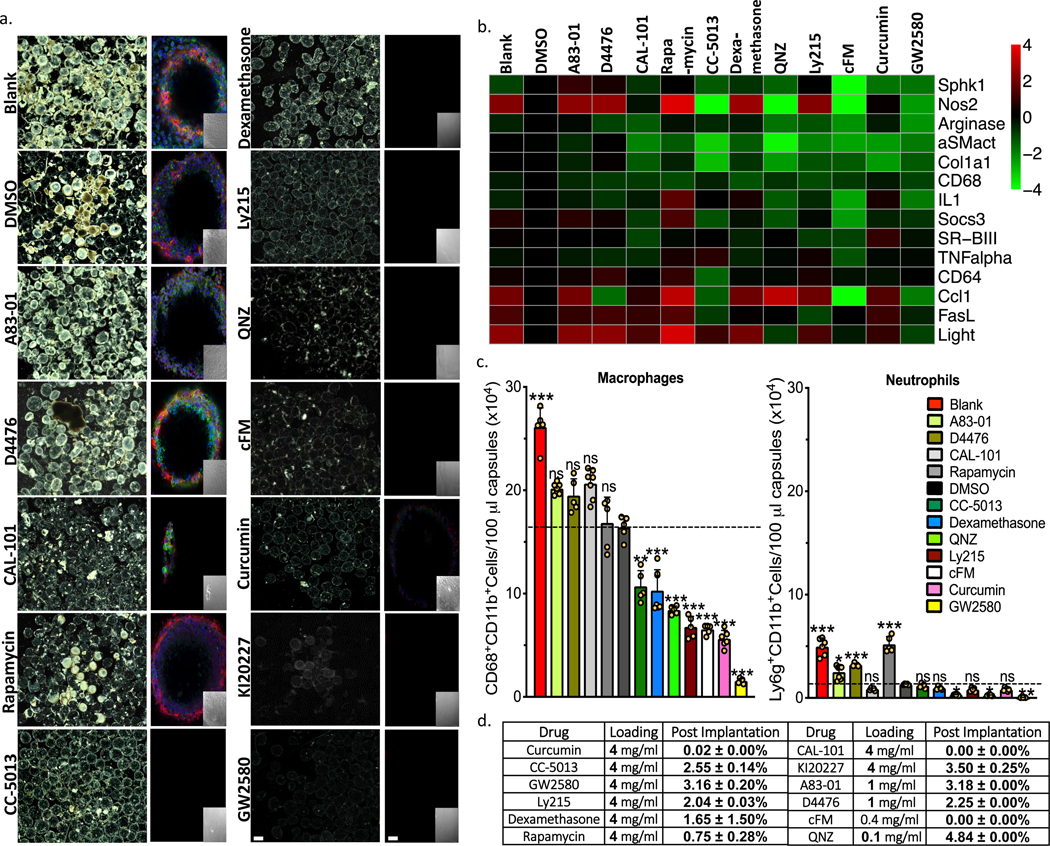
Figure 1. Anti-fibrotic drug screen. Testing agents largely targeted to macrophage biology.
a) Phase contrast and confocal images, respectively, of capsules (Blank, DMSO vehicle, or containing amorphous drug, as indicated) retrieved following implantation into the IP space of C57BL/6 mice for two weeks. Phase contrast images showing host FBR immune cell adhesion and fibrosis Confocal microscopy images showing reduced or no fibrotic overgrowth on alginate microcapsules (Blue, DAPI nuclear stain; Green:cellular cytoskeleton marker F-actin; and Red:Fibrosis marker αSMactin. Insets:brightfield images of the same fields of view in the main confocal panel). Scale bars, phase contrast:500μm; confocal image:50μm. b) Multiplexed NanoString gene expression analysis of macrophage subtyping and Fibrosis markers for RNA isolated from the surface of free-floating Blank (no drug), drug vehicle (DMSO-for amorphous formulations), and amorphous drug loaded microsphere capsules, following a 2-week implantation in C57BL/6 mice. Interestingly, both cFM and GW2580 target CSF1R, and show almost identical gene expression responses. Red:increase in expression; Green:decrease in expression, as compared to vehicle (DMSO)-loaded. c) Quantitative FACS analysis of macrophage and neutrophils respectively performed on cells dissociated directly off of alginate spheres. Some drugs significantly reduced macrophage and neutrophils presence. Data:mean±SEM. d) Table showing that all compounds, encapsulated in their amorphous form, either ran out or had less than 5% drug remaining after only a 2-week IP implantation in C57BL/6 mice. All bar graph data:mean±SEM. Statistical analysis:one-way ANOVA plus Bonferroni multiple comparison correction; *:p<0.05; **:p<0.001, and ***:p<0.0001; ns=not significantly different. For all in vivo data, N=5 mice/group. All subpanels reflect representative data from in vivo experiments repeated 3 times.