Figure 4. Signal integration in NSCs.
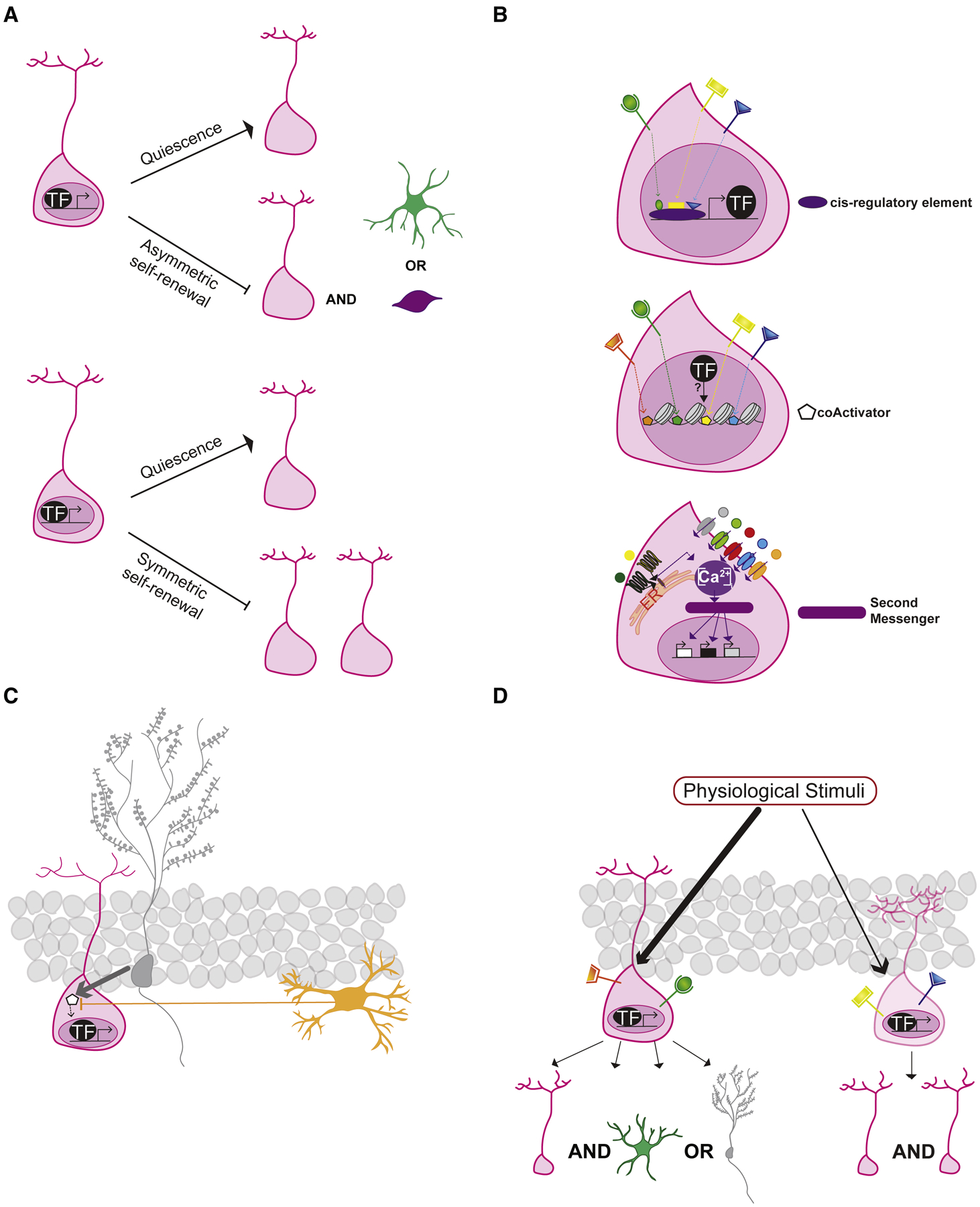
NSCs filter and integrate a wide-range of signals to make activation and division decisions. a. Master TFs may couple maintenance of NSC quiescence with repression of asymmetric stem cell renewal or symmetric stem cell renewal. b. Distinct physiological signals may converge onto the same cis regulatory element (purple) to regulate expression of master transcription factors (black) and influence the expression of target genes (white) involved in NSC quiescence-activation, fate choice and self-renewal (top). Distinct signals may recruit different coactivators (orange, green, yellow, blue) that bias master TF occupancy (black circle) at target gene promoters resulting in differential expression of genes (middle). Levels of intracellular calcium may mediate different biological responses in NSCs. Ca2+ influx into the cytoplasm from the extracellular environment (grey, green, red blue and orange receptors) and from the endoplasmic reticulum [G protein coupled receptors (dark green and yellow) and ER (light orange)] contribute to intracellular levels of calcium that, through the activation of second messengers, can mediate distinct cellular behaviors (bottom). c. The spatial organization of the niche can influence signal integration in NSCs. For example, a signal released by a DGC (grey) proximal to the NSC (pink) outcompetes an antagonistic signal released by distally located microglia (orange). d. Phenotypic and functional diversity of NSCs in the niche may support distinct fate choices i.e. bias towards asymmetric neurogenic or astrogenic stem cell renewal or symmetric stem cell renewal. See text for details.
