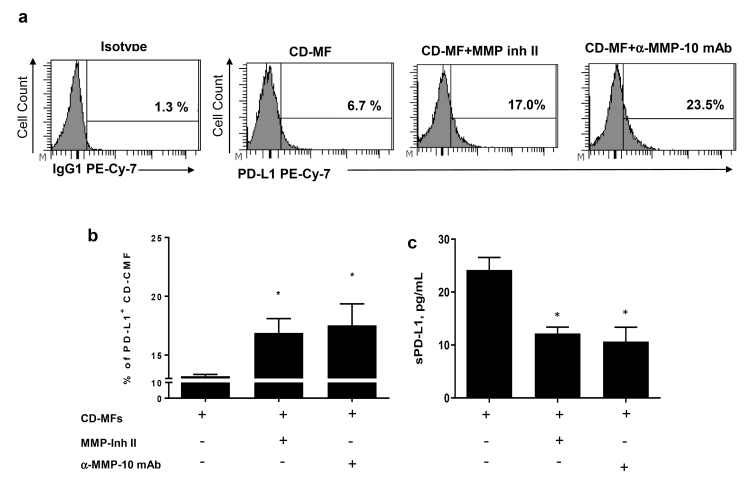
Fig. 4.
The proteolytic activity of MMPs contributes to the reduction of the mPD-L1 on cell surface of CD-MFs. Primary human isolates of CD-MFs were treated or not with the 30 nM of MMP Inhibitor II (CAS 203915-59-7) or anti-human MMP-10 mAbs (clone LA-12) for 72 h, then immunostained and used for multi-color flow cytometry. Live events were gated based on forward and side scatters, as well negativity for the incorporation of the viability dye (conjugated to eFluor™ 780) and were analyzed for the surface expression of mPD-L1. (a) Representative histograms and (b) summary of the flow cytometry analysis show that expression of mPD-L1 is reduced on cell surface of CD-MFs. (c) Summary of sPD-L1 shows an increase in sPD-L1 in the conditioned media from CD-MFs. Addition of broad spectrum MMP Inhibitor-II, which targets MMP-1, -3, -7, -9 or anti-MMP-10 mAb restores mPD-L1 level on the surface of CD-MFs and decreases sPD-L1 concentration in the condition media derived from these cells. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 4, *P < 0.05.