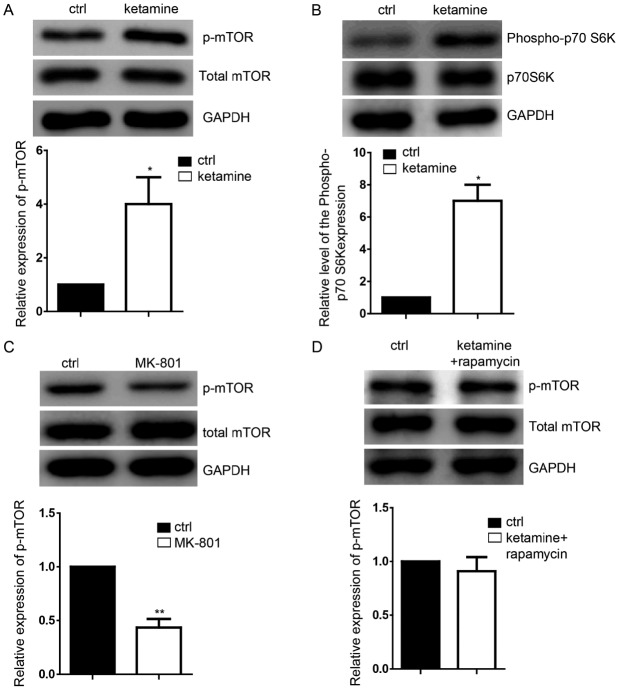
Figure 2.
Ketamine activates the mTOR signaling pathway. (A) Representative images of the expression of p-mTOR in neural progenitor cells derived from ESCs as detected by western blotting; the ratio of p-mTOR normalized to GAPDH/total mTOR is presented. (B) Ketamine-treatment group demonstrated the upregulation of p-70SK6. (C) Inhibtion of the NMDA signaling pathway by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 decreased the expression levels of p-mTOR; the ratio of p-mTOR normalized to GAPDH/total mTOR is presented. (D) 50 µM rapamycin markedly reduced the activation of the mTOR signaling, which attenuated the function of ketamine on regulating the level of p-mTOR. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. the ctrl. Ctrl, control; ESC, embryonic stem cell; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; p, phosphorylated.