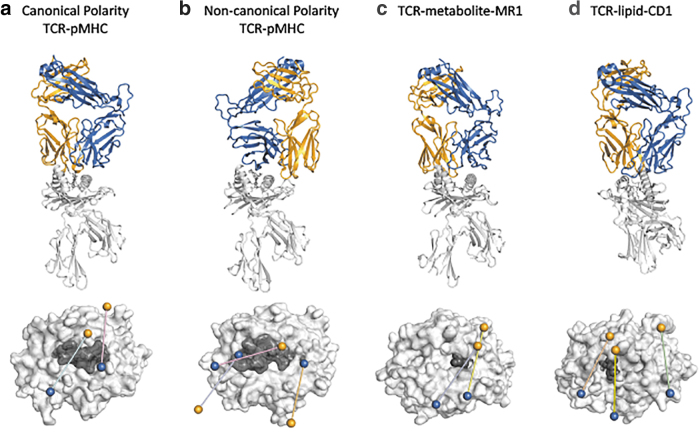
FIG. 1.
Comparison of docking orientations for TCR-MHC and MHC-like interactions. Above: Ribbon structures of selected TCR-MHC and TCR-MHC-like interactions. Bottom: Top view of the TCR docking footprint on top of the MHC or MHC-like molecule. Orange and blue spheres represent the centers of mass for TCRα and TCRβ variable domains, respectively. The MHC molecule is colored light gray and the antigen is colored in dark gray. (a) Canonical docking topology of the LC13-HLA-B8EBV complex (above) and the footprints of the LC13 TCR (cyan; PDB: 1MI5) and the “superbulged” peptide-centric TCR SB27 over HLA-B*3508EBV (pink; PDB: 2AK4) (bottom). (b) Noncanonical topology of the reversed NP1-B17-H-2DbNP366 complex (above) and the footprints of the NP1-B17 TCR (blue; PDB: 5SWZ), the reversed FS18 TCR over HLA-DR4proinsulin (orange; PDB: 4Y19), and the nonsignaling 42F3 TCR over H-2:Ldp3A1 (pink; PDB: 3TJH) (bottom). (c) Unconventional MAIT M33.64-MR15-OP-RU complex (above) and the footprints of the MAIT M33.64 TCR (yellow; PDB: 5D5M) and MAV36 TCR over MR15-OP-RU (blue PDB: 5D7L) (bottom). (d) Unconventional 3C8-CD1cmonoacylglycerol complex (above), and the footprints of the 3C8 TCR (wheat; PDB: C09), the BK6 TCR over CD1aLPC (green, PDB: 4X6C), and the PG90 TCR over CD1bPG (blue; PDB: 5WKI) (bottom). EBV, Epstein-Barr Virus; HLA, human lymphocyte antigen; MAIT, mucosal associated invariant T; PDB, Protein Data Bank; TCR-MHC, T cell receptor-major histocompatibility complex.