Table 1.
Small molecule JNK inhibitors identified in high throughput screening of proprietary chemical libraries
| Core structure/Class description in initial publications | Inhibitor Structure (note: Compound number refers to that given in the original report) | Identification | IC50 (and/or Ki when reported) | PDB entry | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthrapyrazolone |
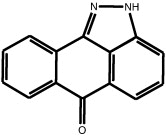 SP600125 SP600125 |
High throughput screening of Celgene compound collection using JNK2 activity assay, followed by cell-based testing | IC50 JNK1 = 40 nM IC50 JNK2 = 40 nM IC50 JNK3 = 90 nM | 1UKI 1PMV | [5] |
| Diaryl-imidazoles |
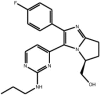
 Compound 1 Compound 1 |
Reported by scientists at Merck, but discovery approach not described. Note, this compound also interacts with and inhibits p38 with higher potency (IC50 p38 = 0.078 nM) | IC50 JNK3 = 7 nM | 1PMN | [5] |
| (Benzoylaminomethyl) thiophene sulfonamides |
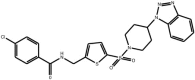 Compound 50a Compound 50a |
High throughput screening of Serono compound collection using JNK3 activity assay, followed by structure–activity relationship studies and neuronal cell based assays for the inhibition of NGF-deprivation-induced cell death. | IC50 JNK2 = 650 nM IC50 JNK3 = 150 nM | – | [58] |
| Dihydro-pyrrolo imidazoles |
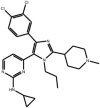
 Compound (S)-5 Compound (S)-5 |
Design by Eisai scientists based on structures of known p38 inhibitors with additions to increase JNK3 inhibitory potency and selectivity; testing inhibition of c-Jun phosphorylation and survival following K+ withdrawal from cerebellar granule neurons. Note, this compound inhibits p38 with lower potency (IC50 p38 = 28 nM) | IC50 JNK1 = 2.5 nM | – | [59] |
| (Benzothiazol-2-yl) acetonitrile |
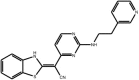 Compound 59 (AS601245) Compound 59 (AS601245) |
High throughput screening of Serono compound collection using JNK3 activity assay, followed by structure–activity relationship studies, cell-based assays and anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. | IC50 JNK1 = 150 nM IC50 JNK2 = 220 nM IC50 JNK3 = 70 nM | – | [60] |
| Anilinoindazoles |
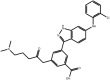 Compound 10 Compound 10 |
High throughput screening of Astra Zeneca compound collection using JNK3 activity assay, followed structure–activity relationship studies. | IC50 JNK1 = 101 nM IC50 JNK3 = 3 nM | 2B1P | [61] |
| Pyrazoloquinolinones |
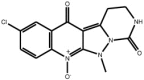 Compound 16 Compound 16 |
High throughput screening of Abbott compound collection using JNK1 activity assay, followed by testing in cell-based assays for inhibition of tumour necrosis-factor stimulated c-Jun phosphorylation | IC50 JNK1 = 290 nM | 2GO1 (structure with a related compound) | [63] |
| Aminopyridines |
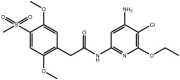 Compound 35 Compound 35 |
High throughput screening of Abbott compound collection using JNK1 activity assay, followed by testing in cell-based assays for inhibition of tumour necrosis-factor stimulated c-Jun phosphorylation | IC50 JNK1 = 36 μM (Ki JNK1 = 3 nM) IC50 JNK2 = 70 μM (Ki JNK2 = 13 nM)(Ki JNK3 = 61 nM) | 2GMX (structure with a related compound) | [64] |
| Pyridine carboxamide |
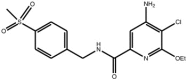 Compound 12 Compound 12 |
High throughput screening of Abbott compound collection using JNK1 activity assay, followed by testing in cell-based assays for inhibition of tumour necrosis-factor stimulated c-Jun phosphorylation. | IC50 JNK1 = 24 nM) IC50 JNK2 = 74 nM) | 2H96 (structure with a related compound) | [65] |
| Anilino-bipyridines |
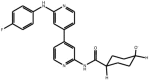 Compound 11 Compound 11 |
High throughput screening of Astra Zeneca compound collection using JNK3 activity assay, followed structure–activity relationship studies. Note, this compound also inhibits p38 with comparable potency (IC50 p38 = 40 nM) | IC50 JNK1 = 88 nM IC50 JNK3 = 15 nM | 2EXC | [62] |
| Anilino-pyrimidines |
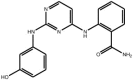 Compound 2b Compound 2b |
High throughput screening of Abbott compound collection using JNK1 activity assay, followed by rational structural design then testing in cell-based assays for inhibition of tumour necrosis-factor stimulated c-Jun phosphorylation. | IC50 JNK3 = 9 nM | 2NO3 | [66] |
