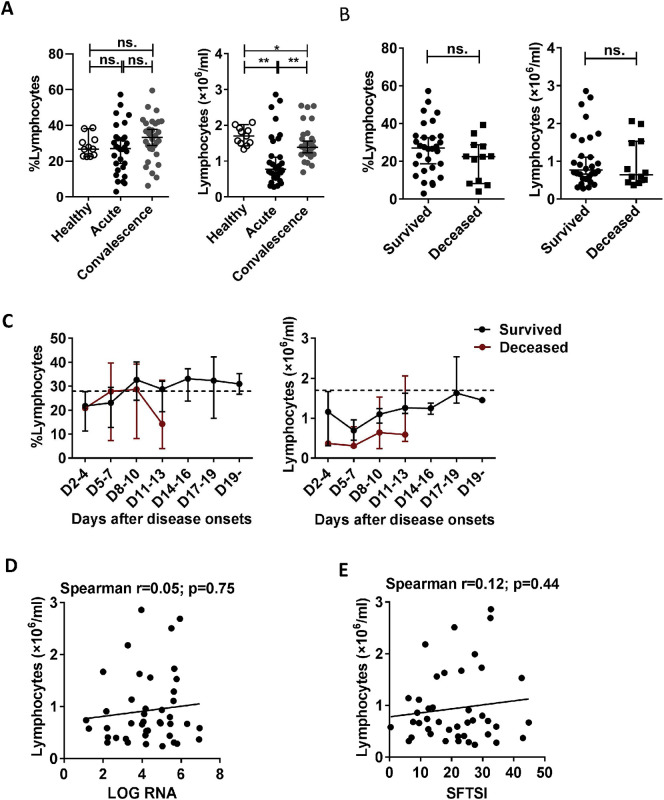
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Changes in the percentage and absolute number of lymphocytes during SFTSV infection in humans. (A): The percentage and number of lymphocytes in the healthy controls (n = 11) and the surviving patients with SFTS in the acute phase (n = 30) and SFTS in the recovery phase (n = 30). (B): The percentage and number of lymphocytes at admission in the surviving patients (n = 30) and deceased patients (n = 12). (C): Dynamic changes in the percentage and number of lymphocytes in the surviving patients (n = 30) and deceased patients (n = 12). These parameters were monitored at the indicated time points for the entire hospital stay of the patients. The dashed line represents the median of the uninfected controls. (D) and (E): Correlation of the number of lymphocytes with the viral load and SFTSI in the SFTS patients (n = 42). Correlation analysis was performed using a non-parametric Spearman correlation test. In the graphs, r and p indicate the correlation coefficient and the p-value of significance, respectively. Data from (A), (B) and (C) are shown as the median ± 95% CI. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann–Whitney U test or Wilcoxon matched pairs test. The level of significance is indicated as follows: ns, not significant; *p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001; ****p < .0001.