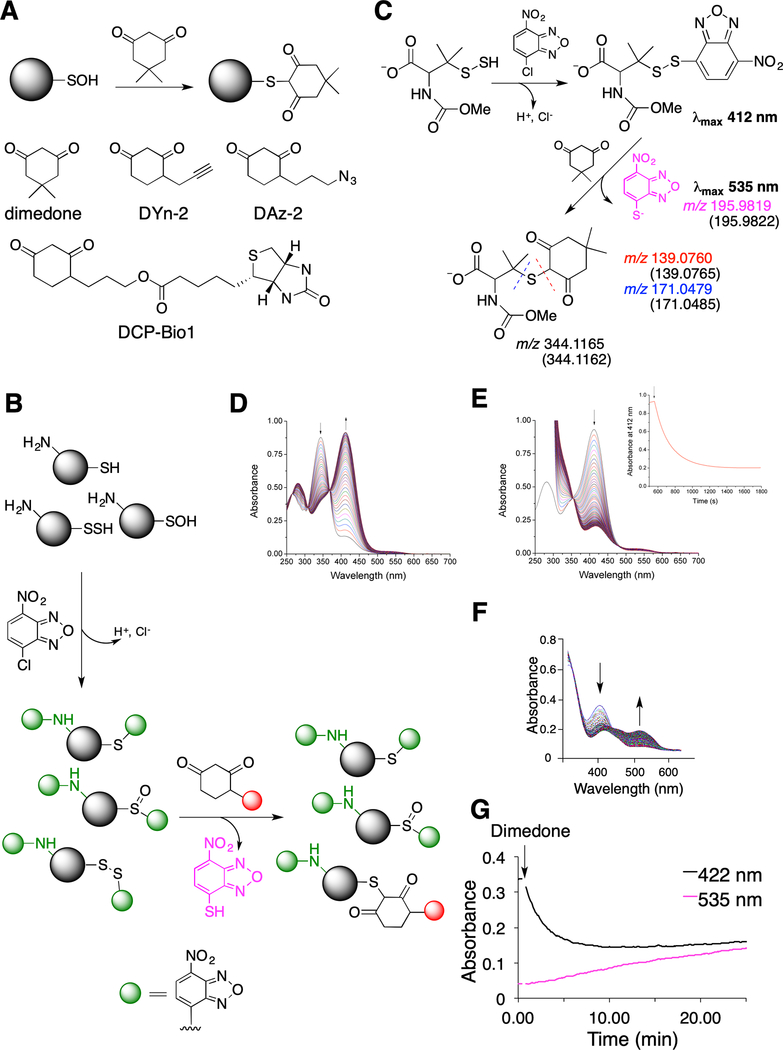
Fig. 1. Probing dimedone switch strategy for persulfide labeling.
(A) (Upper) Labeling of sulfenic acids with dimedone. (Lower) Structures of dimedone-based probes.
(B) Proposed dimedone switch strategy for persulfide labeling. In the first step proteins react with 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzofurazan (NBF-Cl) to label persulfides, thiols, sulfenic acids, and amino groups. Reaction with amino groups gives characteristic green fluorescence. In the second step, NBF tag is switched by a dimedone-based probe, selectively labeling persulfides.
(C) Model switch reaction with 100 μM N-methoxycarbonyl penicillamine persulfide (nmc-PSSH) and 100 μM NBF-Cl, followed by 500 μM dimedone. MS analysis reveals formation of 4-thio-7-nitrobenzofurazan (535 nm) and dimedone labeled nmc-penicillamine, which under MS/MS conditions decomposes along the blue or red dash line. Numbers given in the brackets represent calculated m/z for the observed ions.
(D) Time-resolved spectra for the reaction of 100 μM nmc-PSSH with 100 μM NBF-Cl (pH 7.4, 23 °C). Arrows indicated disappearance of NBF-Cl and appearance of nmc-PSS-NBF adduct at 412 nm.
(E) Time-resolved spectral changes upon addition of 200 μM dimedone to a reaction mixture shown in (D) (pH 7.4, 23 °C). Inset: Kinetics of decay of 412 nm absorbance maximum after addition of dimedone.
(F-G) 23 μM HSA-SSH was left to react with 100 μM NBF-Cl over 30 min in phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.4) with 1% SDS, at 37 °C and then 200 μM dimedone was added. UV-Vis spectral changes (F) and kinetic traces (G) show the decay of the 422 nm absorbance and the appearance of a 535 nm peak.