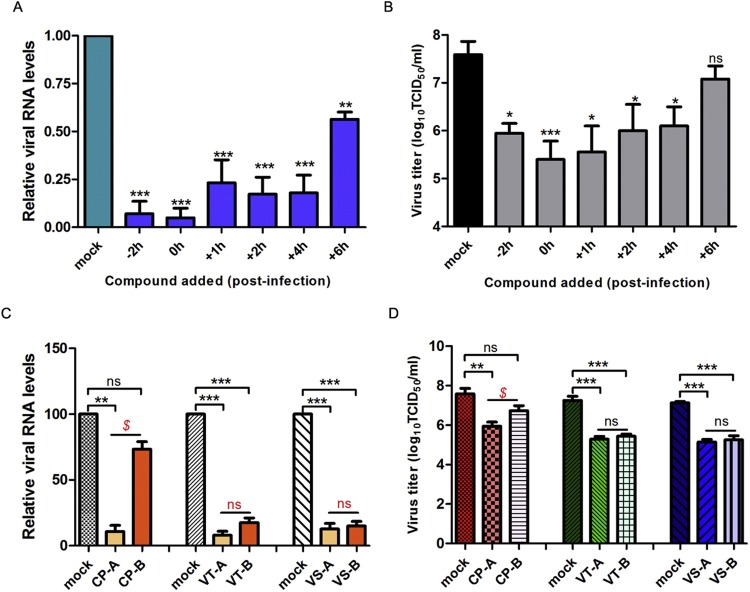
Fig. 2.
Analysis of the preliminary antiviral mechanism for IOP.
(A, B) CRFK cells (104) were infected with strain F9 at an MOI of 0.01. IOP (60 μg/mL) was added to the cells at −2 h, 0 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h and 6 h. Viral RNA (A) and titers (B) were analyzed at 24 hpi. (C, D) CRFK cells were pre-treated with 100 μL of IOP (60 μg/mL) or DMEM (mock) for 2 h before infection in the CP-A and CP-B groups. In the CP-A group, the medium was not changed, and strain F9 at an MOI of 0.01 was directly added. In the CP-B group, the cells were washed and virus at an MOI of 0.01 was added. After one-hour absorption at 37 °C, fresh DMEM containing 1% FBS was added into the CP-A and CP-B groups. For the VT-A and VT-B groups, 100 μL of IOP (60 μg/mL) or DMEM (mock) and 10 μL of strain F9 (an MOI of 0.01 when added into cells) were mixed and incubated at 4 °C for one hour before the mixture was added to the cells. After one-hour absorption at 37 °C, the cells were washed, and fresh DMEM containing 1% FBS and IOP (60 μg/mL) or containing only 1% FBS was added into VT-A and VT-B groups, respectively. For the VS-A and VS-B group, 100 μL of IOP (60 μg/mL) or DMEM (mock) and 10 μL of strain F9 (an MOI of 0.01 when added into cells) were mixed and then the mixture was directly added to the cells. After one-hour absorption at 37 °C, the cells were washed, and fresh DMEM containing 1% FBS and IOP (60 μg/mL) or containing only 1% FBS was added to the VS-A and VS-B groups, respectively. Viral RNA (C) and titers (D) were analyzed at 36 hpi. Results represent the mean of three replicates ± SD, and each experiment was repeated three times.