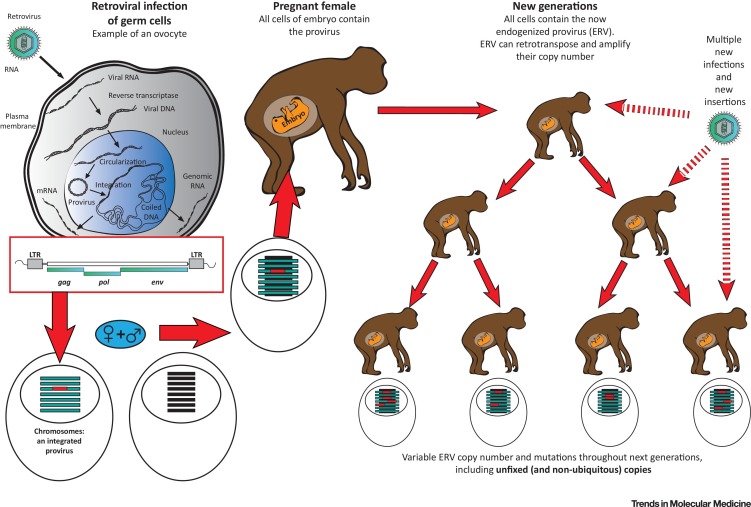
Figure 2.
Successive Steps Leading to Endogenization of Retroviruses and to Multicopy Endogenous Retroviral (ERV) Families in Descendants. This illustration depicts the successive steps of retroviral endogenization, starting from infection of gametes, integration of a DNA retroviral copy (provirus) into a chromosome, giving birth to a viable individual inheriting and retaining this copy in the DNA of all cells and transmitting this to its offspring. Throughout successive generations and evolution, both endogenous retrotranspositions and reinfections of the germline of particular individuals (provided that the exogenous strain persists in the environment) generates multiple and variable copy numbers in the final population. This variability has been well known in some animal species and has recently also been evidenced in humans [91]. Abbreviations: env, envelope; gag, group-specific antigen; LTR, long terminal repeat; pol, polymerase.