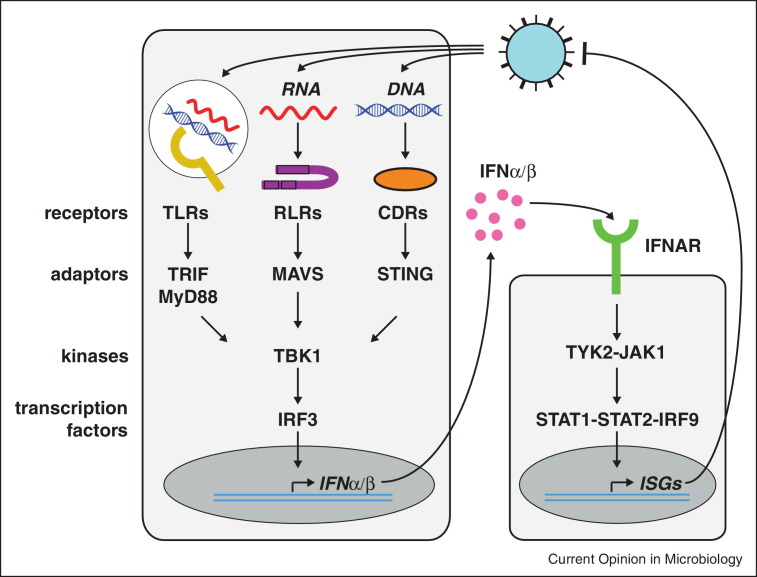
Figure 1.
Induction and effects of IFN during virus infection. Virus infection delivers nucleic acids into the cytosol or endosomal compartment. Innate nucleic acid sensors including TLRs, RLRs and the poorly characterized cytosolic DNA receptors (CDRs) detect these DNAs and RNAs and then trigger a signal transduction cascade that induces IFN. Adaptor proteins, kinases and transcription factors mediate signalling. Note that additional proteins have been implicated and that the figure only shows some selected key components. IFN signals via IFNAR resulting in the induction of ISGs that have direct and indirect anti-viral effects.