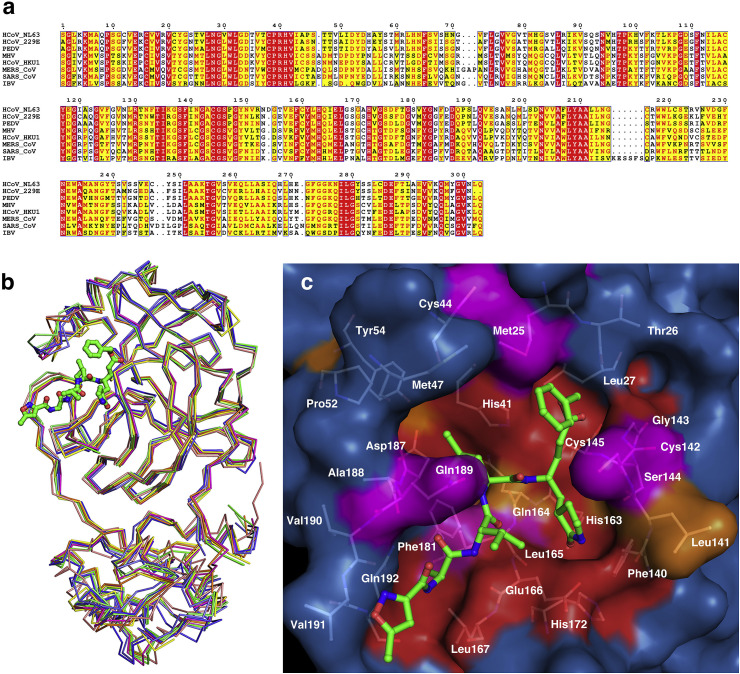
Fig. 3.
Structural conservation analysis of Mproamong CoVs.
(a) Sequence alignment of Mpro from MHV-A59 and 7 various CoVs: HCoV-229E, HCoV-HKU1, HCoV-NL63, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, PEDV and IBV. (b) Superposition of Mpro from MHV-A59 and 7 various CoVs in complex with peptide substrate analogs (MHV-A59, green; HCoV-NL63, blue, PDB ID 5GWY; HCoV-HKU1, magenta, PDB ID 3D23; SARS-CoV, salmon, PDB ID 2AMQ; MERS-CoV, orange, PDB ID 5WKK; HCoV-229E, lime, PDB ID 2ZU2; PEDV, slate, PDB ID 5GWZ; IBV, yellow, PDB ID 2Q6F). (c) Surface representation of conserved substrate-binding pockets from various CoV Mpros. The background is MHV-A59 Mpro. Red: identical residues; orange: substitution in one CoV Mpro; magenta: substitution in two CoV Mpros; residues involved in N3 binding are shown as white sticks. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)