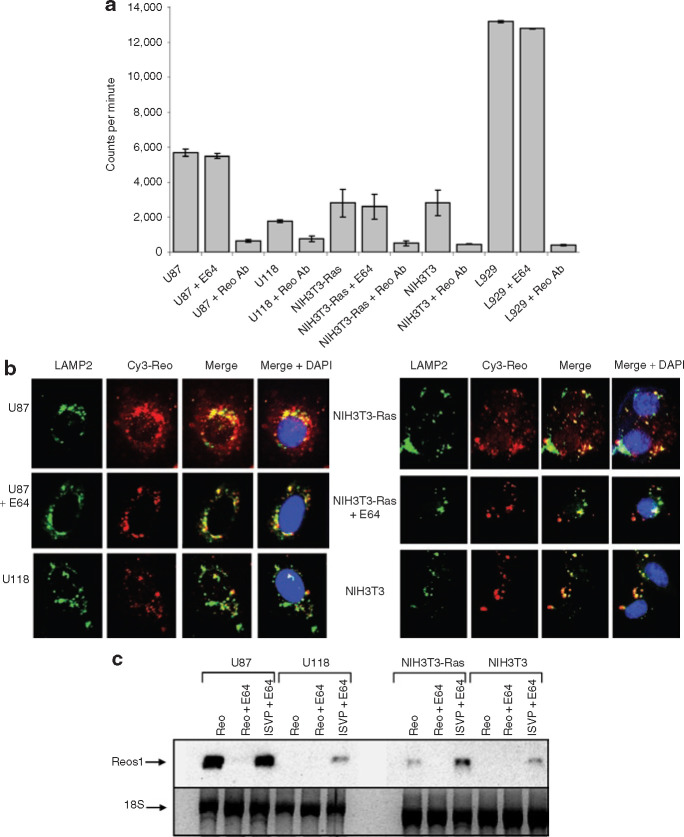
Figure 2.
Assessment of reovirus binding, internalization, and viral transcription in susceptible and resistant cell lines. (a) [35S]-labeled reovirus was allowed to bind on cells in minimal medium for 1 hour at 4°C. Cells were washed twice in phosphate-buffered saline and lysed in a sonification buffer. Samples were subjected to scintillation counting, which was performed in triplicate. (b) Cy3-labeled reovirus at a multiplicity (MOI) of infection of 5,000 was added for 24 hours to cells grown on glass slides, after which cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde. Immunofluorescence with the lysosomal marker lysosomal associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2) antibody followed by secondary fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) was performed; slides were then mounted with a 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) mounting medium (VECTOR) and photographed by multiple acquisition with a fluorescent Zeiss microscope (magnification ×400). (c) Total RNA from cells were purified using the RNeasy RNA extraction kit; equal RNA amounts were subjected to Northern blotting using a digoxygenin-labeled probe against the positive strand of reovirus S1 transcripts. ISVP, infectious subviral particle.