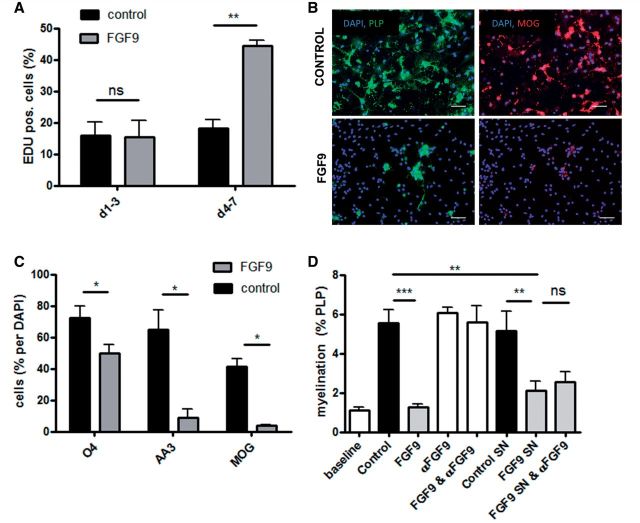
Figure 5.
FGF9 inhibits OPC differentiation directly and induces secretion of myelination-inhibiting factors by astrocytes. Proliferation of immunopurified A2B5+ OPCs cultured in the presence or absence of FGF9. FGF9 is not initially an OPC mitogen (DIV 1–3), but progenitors become responsive as they differentiate (DIV 4–7) (A). This proliferative response is associated with inhibition of OPC differentiation assessed using three stage specific markers (O4, PLP and MOG) (B and C). B provides representative images demonstrating the effect on expression of PLP and MOG. Scale bar = 100 µm. Supernatants from FGF9 treated and untreated neurosphere-derived astrocytes were harvested and added to myelinating cultures in the presence or absence of a neutralizing anti-FGF9 antibody (10 μg/ml) from 18 to 28 DIV (D). Quantifying PLP+ myelination reveals the FGF9-specific antibody neutralized the ability of FGF9 to inhibit myelination, but failed to block inhibitory activity present in supernatants harvested from FGF9-treated astrocytes. (A, C and D) Data represent means ± SEM from at least three independent experiments; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, n.s. = not significant.