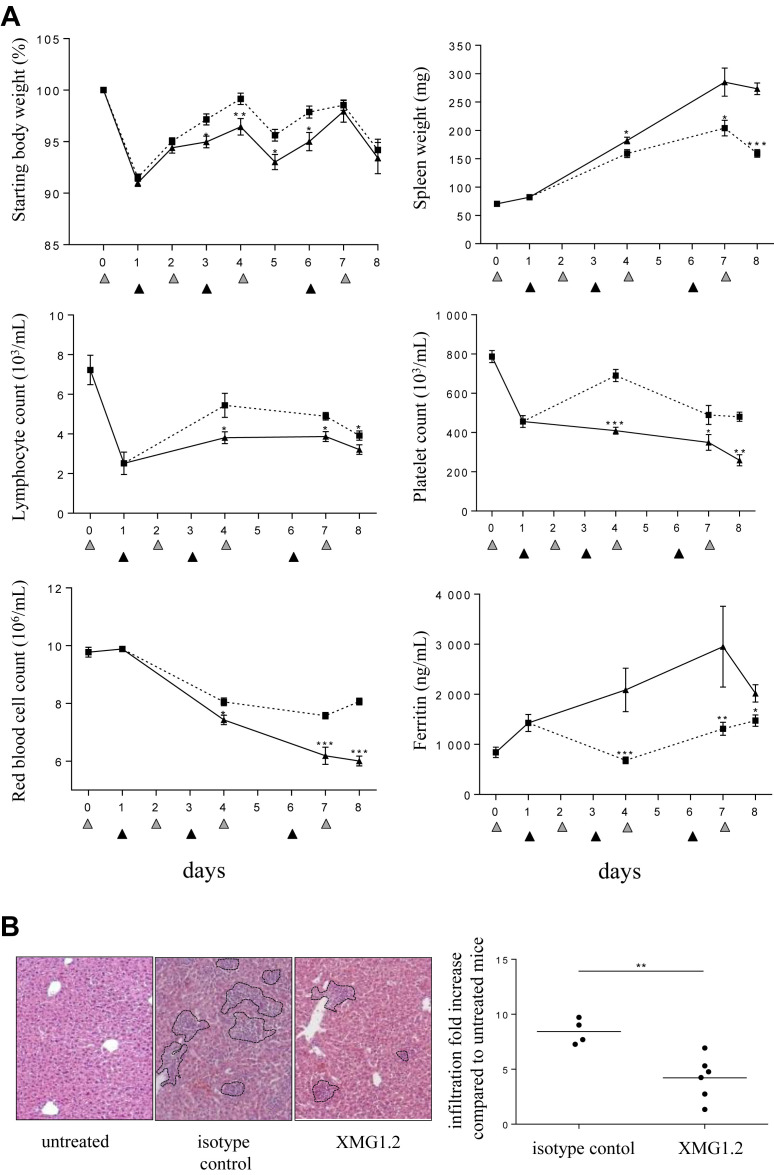
Fig 4.
IFNγ is required for hematological and tissue parameters in the model of sHLH. Mice (n = 8 per time point) were injected with 50 μg of CpG-ODN at days 0, 2, 4, and 7 (gray filled triangles) and administered 100 mg/kg of the anti-IFNγ mAb, XMG1.2 (dotted line), or with an isotype control mAb (solid line), on days 1, 3, and 6 (black filled triangles). (A) Body and spleen weights were monitored, and blood parameters, including lymphocyte, platelet, and red blood cell counts, were measured using a hemavet analyzer. Serum ferritin was measured by ELISA. The samples from day 0 were collected before the CpG-ODN injection, whereas samples from day 2, 4, and 7 were collected 6 hours after CpG-ODN injection. Samples from the day of a mAb administration were collected before the injection. Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean. Data are representative of 2 experiments. Statistics were performed at each time point between isotype control and XMG1.2-treated group values. (B) Liver inflammation was evaluated on day 8 by calculating the area that contained foci of leukocyte infiltration as illustrated by the outlined areas in the representative photomicrographs of H and E-stained sections (Zeiss Axiovert 40 CFL; Zeiss AxioCam MRc Rev.3; original magnification ×100) from an isotype control or XMG1.2-treated mouse. The graph represents the quantitative analysis of at least 9 fields per liver capturing the fold increase of area as compared to untreated mice (ie, no CpG injection); each symbol represents an individual mouse; horizontal lines represent the mean values. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 were obtained using the 1-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney U t test. IFNγ, interferon γ; sHLH, secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.