Figure 4.
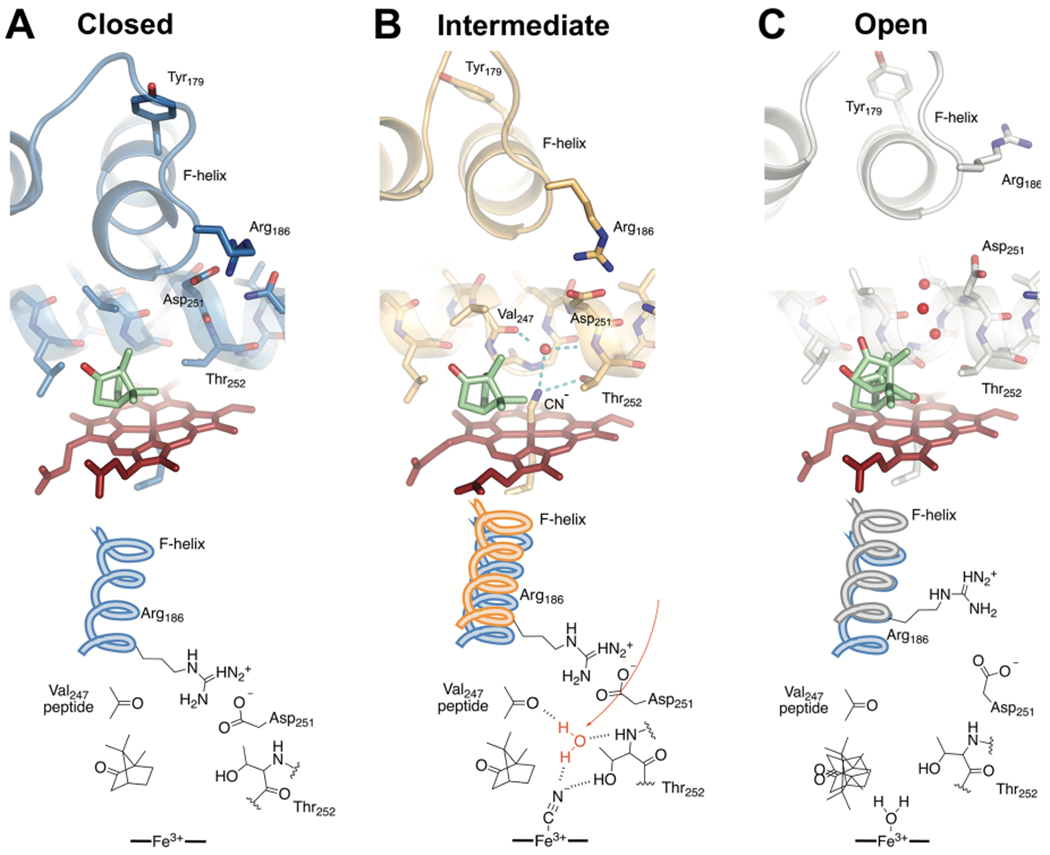
Comparisons of the active site structures predicted from cluster analysis of MD trajectories. Shown are the closed camphor/P450cam (A), intermediate CN−/camphor/P450cam/Pdx (B), and open camphor/P450cam/Pdx (C) complexes representing the most highly populated cluster in each MD simulation. Camphor and heme are shown as green and red sticks, respectively. Water oxygen atoms are shown as red spheres. The bottom panel shows important differences in the interactions at the active site. Both the closed and intermediate structures have an intact ion pair interaction between Arg186 and Asp251. The partially retracted F helix in the intermediate structure (B) provides new interactions with the I helix and the ion pair to favor reorientation of Thr252 and population of the catalytic water (red). We propose this represents the conformation competent for hydroperoxy bond cleavage in the formation of compound I.
