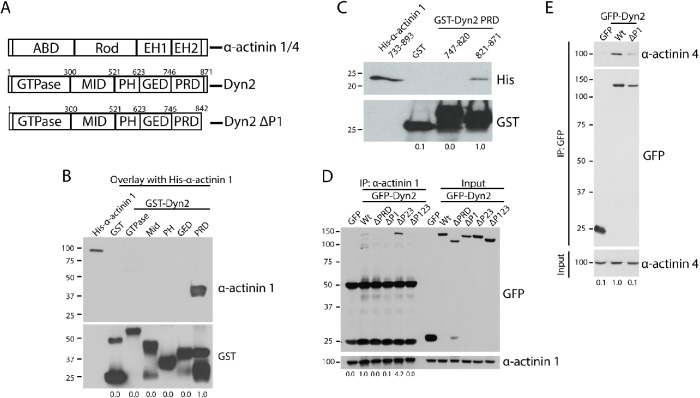
FIGURE 2:
The P1 region in the Dyn2 PRD binds to α-actinin 1 and 4. (A) Schematic diagrams showing the domain structure of Dyn2 and both α-actinin 1 and 4. The α-actinin proteins contain an actin-binding domain (ABD), a rod domain, and two calmodulin-like EF-hand domains (EH1/2). Dyn2 contains a GTPase domain, a middle domain (MID), a pleckstrin-homology domain (PH), a GTPase effector domain (GED), and a proline-rich domain (PRD). Also depicted is the Dyn2 ΔP1-binding mutant that does not bind to α-actinin 1/4 (rat Dyn2: Δ843-871; human Dyn2: Δ846-869). (B) An overlay binding assay was used to test which domain of Dyn2 binds to full-length His–α-actinin 1. GST was used as a control to show no binding. n = 3 independent experiments. (C) GST pull down of the N-terminal half of the Dyn2 PRD (amino acids 747–820) and the C-terminal half (amino acids 821–870) was performed to test direct binding with His–α-actinin 1 EH1/2 domains. n = 3 independent experiments. (D, E) Immunoprecipitation of α-actinin 1 (D) or α-actinin 4 (E) from cells expressing different GFP-Dyn2 deletion mutants was performed to determine the α-actinin binding region in the Dyn2 PRD. The Dyn2 deletion mutants tested were deletion of the entire PRD (amino acids 747–871), deletion of the P1 region (amino acids 843–871), deletion of the P2-3 region (amino acids 820–844), and deletion of the P1-P3 region (amino acids 820–871). n = 4 independent experiments (n = 2 independent experiments for GFP-Dyn2 ΔP123). (E) Binding with α-actinin 4 was tested with GFP-Dyn2 WT and GFP-Dyn2 ΔP1 using a GFP-Trap pull down. n = 4 independent experiments. For B–E, relative average binding values are listed below each condition.