FIGURE 6:
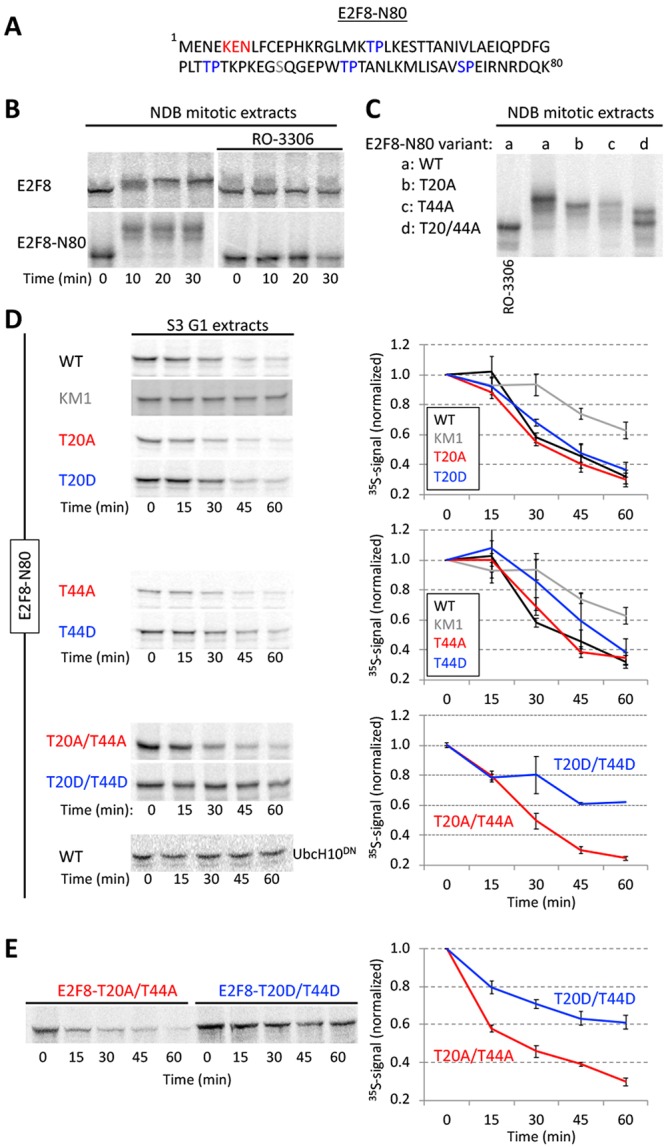
Phosphomimetic Cdk1 sites stabilized E2F8 in G1 extracts. (A) E2F8 N-terminal fragment of 80 amino acids (E2F8-N80). KEN box and four canonical Cdk1 consensus phosphorylation sites are colored. (B) Time-dependent electrophoretic mobility shift of full length- and E2F8-N80 (35S-labeled IVT products) in NDB mitotic extracts supplemented with mock or the Cdk1 inhibitor RO-3306. (C) Thr (T)20 and/or T44 of E2F8-N80 were substituted with Ala (A). Mobility shifts of WT vs. mutant E2F8-N80 variants are shown. (D) Time-dependent degradation in G1 extracts of E2F8-N80 and the following variants: KEN box mutant (KM1), single/double phosphomimetic mutants (T-to-Asp [D]), and single/double phospho-dead mutants (T-to-A). (E) Time-dependent degradation of full-length E2F8 carrying double phosphomimetic or double phospho-dead mutations. (B–E) Protein degradations and electrophoretic mobility-shifts were assayed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. A set of source data is shown. Mean and SE calculated from three degradation assays are plotted.
