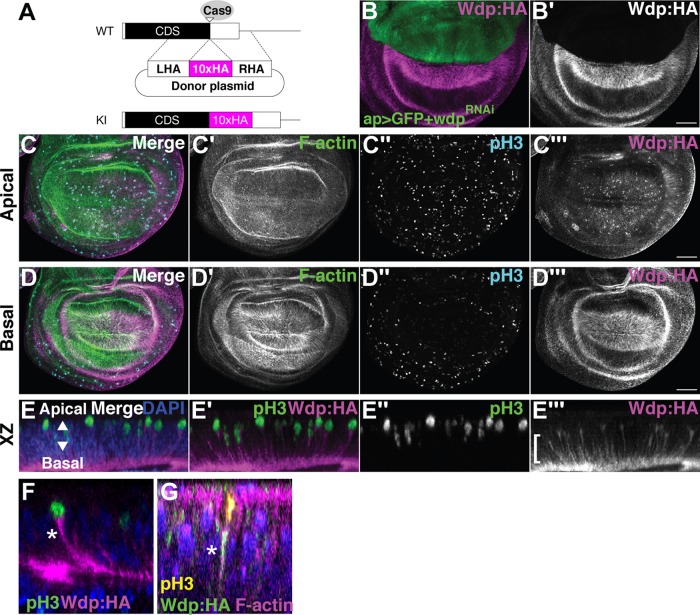
FIGURE 4:
Wdp expression in the wing disc. (A) Schematic of CRISPR–Cas9-mediated gene editing of wdp for generating wdpKI.HA. Ten copies of an HA epitope tag (smGFP-HA) were inserted in frame near the stop codon of the wdp coding sequence (CDS). Only the last exon is shown. CDS, the black box; smGFP-HA, the magenta box; LHA, left homology arm; RHA, right homology arm; Cas9 target site, the open triangle. (B) Anti-HA staining of a wing disc from ap-GAL4 UAS-GFP wdpKI.HA/UAS-wdpRNAi. Wdp:HA is not detectable in the dorsal compartment of a wing disc expressing wdpRNAi (TRiP.HMC06302) with ap-GAL4. (C, D) A wing disc homozygous for wdpKI.HA was stained with Alexa Fluor 568–conjugated phalloidin (F-actin), anti–phospho histone H3 antibody (pH3, mitotic nuclei), and anti-HA antibody. Apical (C) and basal (D) sections of the same disc are shown. Intense staining of Wdp:HA was observed in mitotic cells (C’’ and C’’’) and on the basal side of wing disc epithelium (D’’’). (E–G) Optical cross-sections of 3D-reconstructed images show the accumulation of Wdp:HA in the basal projection (bracket) of apically translocating mitotic cells (E–E’’’). Wdp:HA staining was particularly strong in the basolateral membrane of mitotic cells (asterisk in F) and is colocalized with F-actin (asterisk in G). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (E–G). Scale bars: 50 µm.