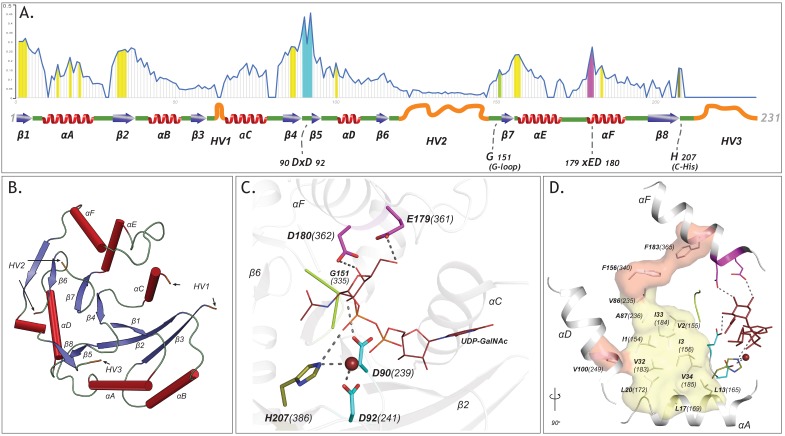
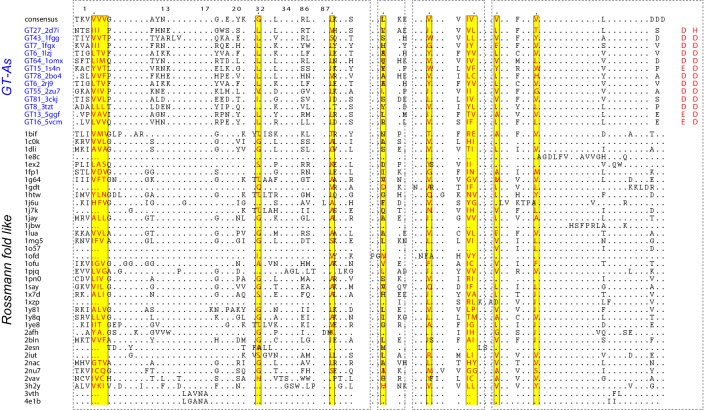
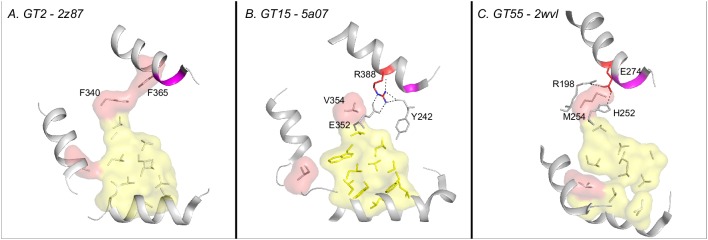
Figure 2. The GT-A common core and its elements.
(A) Plot showing the schematics of the GT-A common core with 231 aligned positions. Conserved secondary structures (red α-helices, blue β-sheets, green loops) and hypervariable regions (HVs)(orange) are shown. Conservation score for each aligned position is plotted in the line graph above the schematics. Evolutionarily constrained regions in the core: the hydrophobic positions (yellow) and the active site residues (DxD: Cyan, xED: Magenta, G-loop: green, C-His: olive) are highlighted above the positions. (B) The conserved secondary structures and the location of HVs are shown in the N-terminal GT2 domain of the multidomain chondroitin polymerase structure fromE. coli(PDB: 2z87) that is used as a prototype as it displays closest similarity to the common core consensus. (C) Active site residues of the prototypic GT-A structure. Metal ion and donor substrate are shown as a brown sphere and sticks, respectively. (D) Architecture of the hydrophobic core (Yellow: core conserved in all Rossmann fold containing enzymes, Red: core elements present only in the GT-A fold). Residues are labeled based on their aligned positions. Numbers within parentheses indicate their position in the prototypic (PDB: 2z87) structure.