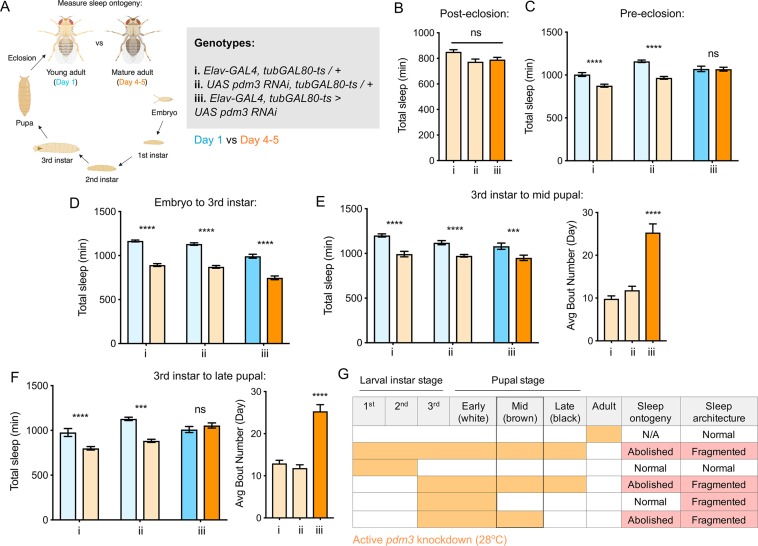
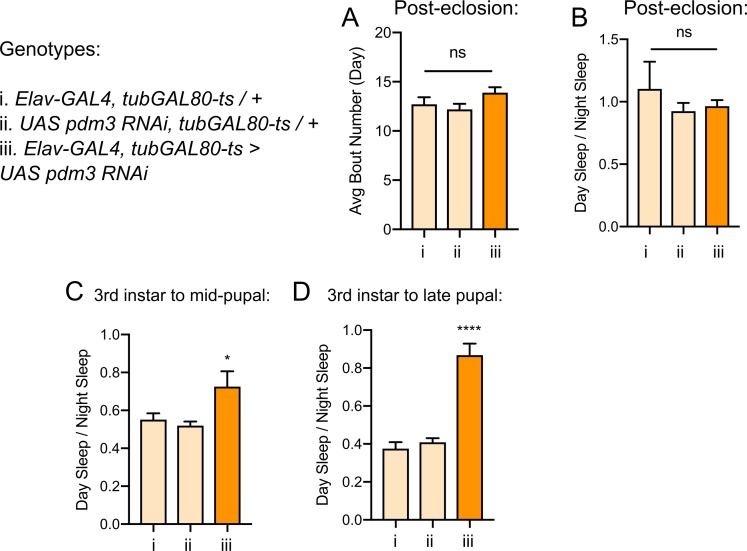
Figure 3. Pdm3 acts during mid-pupal development to control sleep ontogeny.
(A) Drosophila life cycle. (B) Total sleep in mature adults with pdm3 knockdown post-eclosion and genetic controls (n = 50, 60, 70 left to right). (C) Total sleep with pre-eclosion pdm3 knockdown in day 1 (blue) versus day 4–5 (orange) (n = 44, 42, 38, 42, 35, 50 left to right) (D) Total sleep with pdm3 knockdown from embryo to the 3rd instar larval stage (n = 76, 79, 82, 64, 73, 99 left to right). (E) Total sleep (left) and day sleep bout number (right) with pdm3 knockdown from the 3rd instar larval stage up to the mid pupal stage (n = 33, 32, 32, 31, 32, 32 left to right). (F) Total sleep (left) and day sleep bout number (right) with pdm3 knockdown from the 3rd instar larval stage to the late pupal stage (n = 30, 32, 32, 32, 32, 31 left to right). (G) Summary of temporal mapping and dissociation of sleep ontogeny from sleep architecture ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05; multiple Student’s t tests with Holm-Sidak correction, alpha = 0.05 (C, D, E/F left); ANOVA with Tukey’s test (B, E/F right).