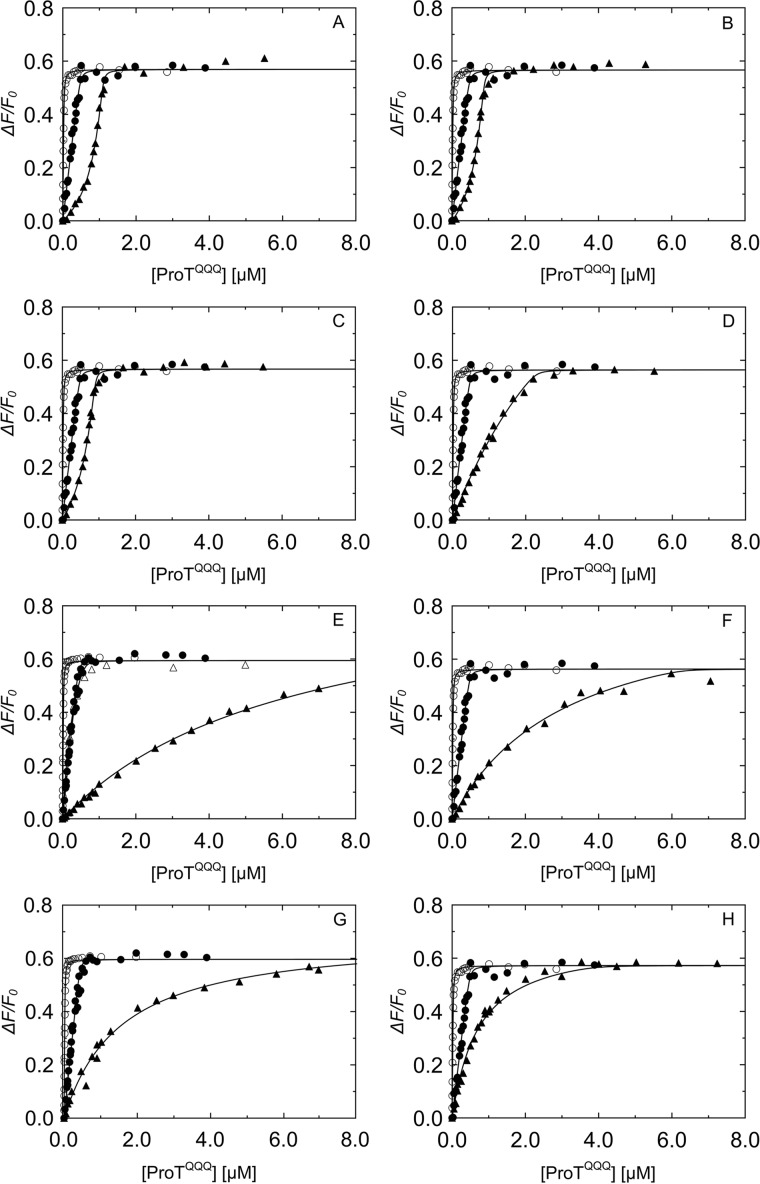
Figure 5.
Competitive binding of SC(1–246) N-terminal double mutants that bind tightly to ProTQQQ. Titrations of the probe, SC(1–246)-BODIPY (29 nm (○) and 502 nm (●)), with ProTQQQ from Fig. 4 served as reference curves for competitive titrations of SC(1–246) mutants. The probe concentration for all of the competitive titrations (▵, ▴) in A–H was 50 nm. Concentrations of competing SC(1–246) mutants were as follows: V1V2 0.90 μm (A), I1A2 0.74 μm (B), L1V2 0.75 μm (C), I1T2 2.24 μm (D), I1W2 0.52 μm (▵) and 9.97 μm (▴) (E), T1V2 6.16 μm (F), L1T2 9.55 μm (G), and L1Q2 3.95 μm (H). Titrations of probe and competitor were simultaneously analyzed by the cubic binding equation to obtain KC, stoichiometry, and maximum fluorescence intensity (ΔFmax/Fo) of the SC(1–246) mutants (Tables 2 and 3).