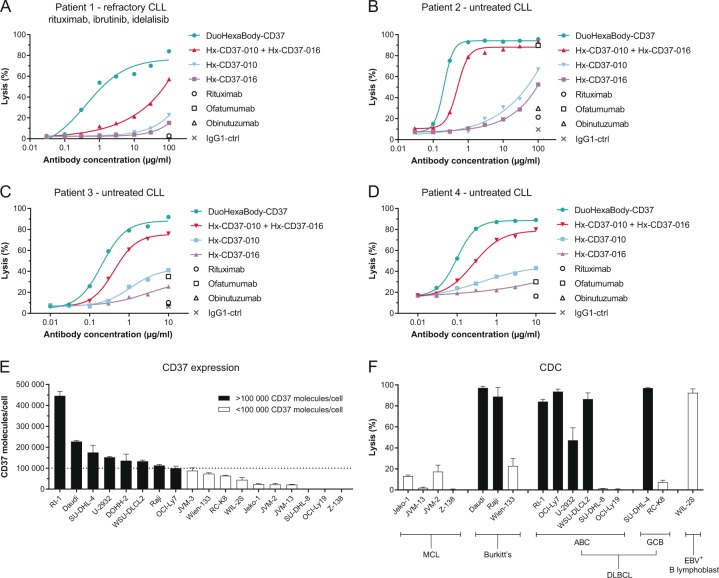
Fig. 3. A biparatopic hexamerization-enhanced CD37 antibody variant, DuoHexaBody-CD37, induces superior CDC activity in vitro and ex vivo.
a–d PBMCs (a, b) or purified B cells (c, d) from four chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients were used to determine CDC induction by DuoHexaBody-CD37, and Hx-CD37 antibody variants (Hx-CD37-010 and Hx-CD37-016) alone or in combination (1:1 equimolar mixture). CDC induction was assessed in the presence of 20% NHS. The percentage lysis was determined by the fraction of PI-positive (a, b) or 7AAD-positive cells (c, d). e 17 B-lymphoma cell lines and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive B-lymphoblastic cell line WIL-2S were evaluated for CD37 molecule expression on the cell surface using quantitative flow cytometry. The dotted line indicates 100,000 CD37 surface molecules/cell. f The capacity of 10 µg/ml DuoHexaBody-CD37 to induce CDC in the presence of 20% NHS was tested in 16 cell lines also described in e and expressed as the percentage lysis determined by the fraction of PI-positive cells. The cell lines are grouped per B-lymphoma subtype: mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Burkitt’s lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with activated B-cell (ABC) or germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtypes and an EBV-positive B-lymphoblastic cell line. Cell lines with >100,000 CD37 molecules per cell are indicated by black bars, and those with <100,000 CD37 molecules per cell by white bars. Either four (e) or two (f) replicates were used per cell line (mean ± SD).