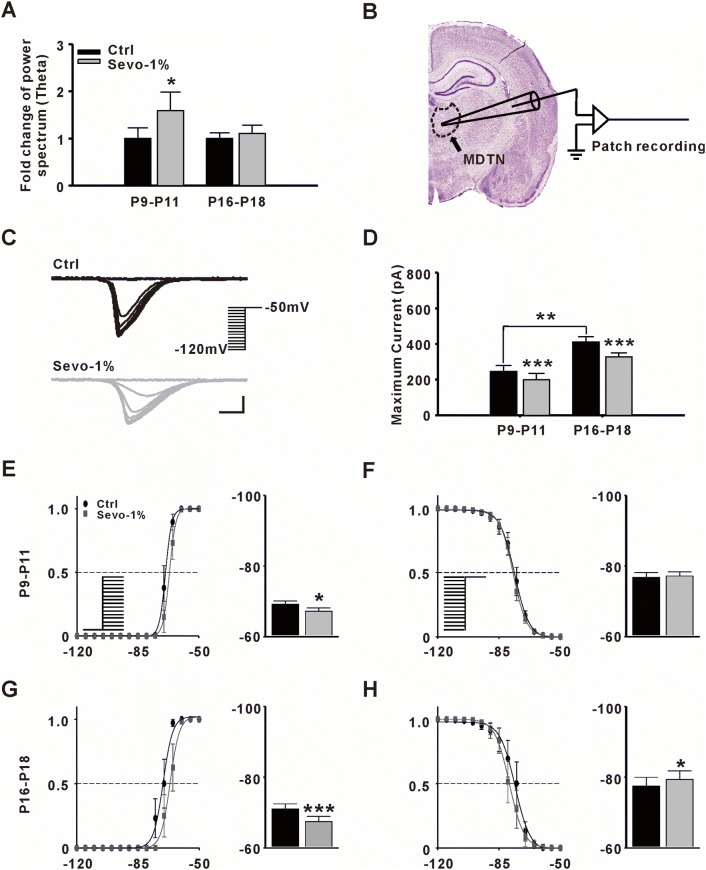
Fig. 4.
Effect of sevoflurane on T-type Ca2+ channel (TCC) currents. A Fold-changes in power spectrum of theta oscillations with 1% sevoflurane (Sevo-1%). A two-minute period of EEG was analyzed before and after a 10-min Sevo-1% application (n = 6, *P ≤ 0.05 vs Ctrl, paired t-test). B Sketch of in vitro patch clamp recording in the medial dorsal thalamic nucleus (MDTN). C Samples of evoked TCC currents from MDTN neurons before (black) and after (gray) Sevo-1% application. TCC currents were gradually inactivated by transient depolarization from various holding potentials to −50 mV (scale bars, 100 pA and 100 ms). D Fold-changes in maximum TCC currents after Sevo-1% application in different groups (n = 8 per group, **P ≤0.01 vs P9–P11, Student’s t-test; ***P ≤ 0.001 vs Ctrl, paired t-test). E, F Steady-state activation/inactivation of TCC currents recorded from the MDTN in younger rat pups (P9–P11) (left panels, activation/inactivation curves; right panels, half-activation/inactivation potentials; n = 8 per group; *P ≤ 0.05 vs Ctrl, paired t-test). G, H Steady-state activation/inactivation of TCC currents recorded from the MDTN in older rat pups (P16–P18) (n = 8 per group; *P ≤ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001 vs Ctrl, paired t-test).