TABLE 1.
Types and properties of generally used synthetic plastics.
| Plastics | Abbreviation | Structure formula | Tm (°C)a | Tg (°C)b | XC (%)c | Recycling codes |
| High-density polyethylene | HDPE | 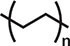 |
200–300 | −120 | 80–90 |  |
| Low-density polyethylene | LDPE | 160–260 | −120 | 45–65 |  |
|
| Polystyrene | PS | 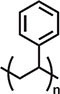 |
240 | 63–112 | – |  |
| Polypropylene | PP | 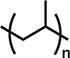 |
130 | −10–18 | 60–70 |  |
| Polyvinyl chloride | PVC | 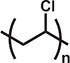 |
100–260 | 60–70 | – |  |
| Polyethylene terephthalate | PET | 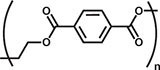 |
260 | 80 | 40–60 |  |
| Polyester polyurethane | Polyester PUR | 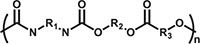 |
8–20 (soft) | −75 to −50 (soft) 185–205 (hard) | 40–50 |  |
| Polyether polyurethane | Polyether PUR | 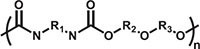 |
-95 (soft) 100 (hard) | −10 to 45 (soft) 190–240 (hard) |
aTm, melting temperature. bTg, glass transition temperature. cXC, crystallinity.
