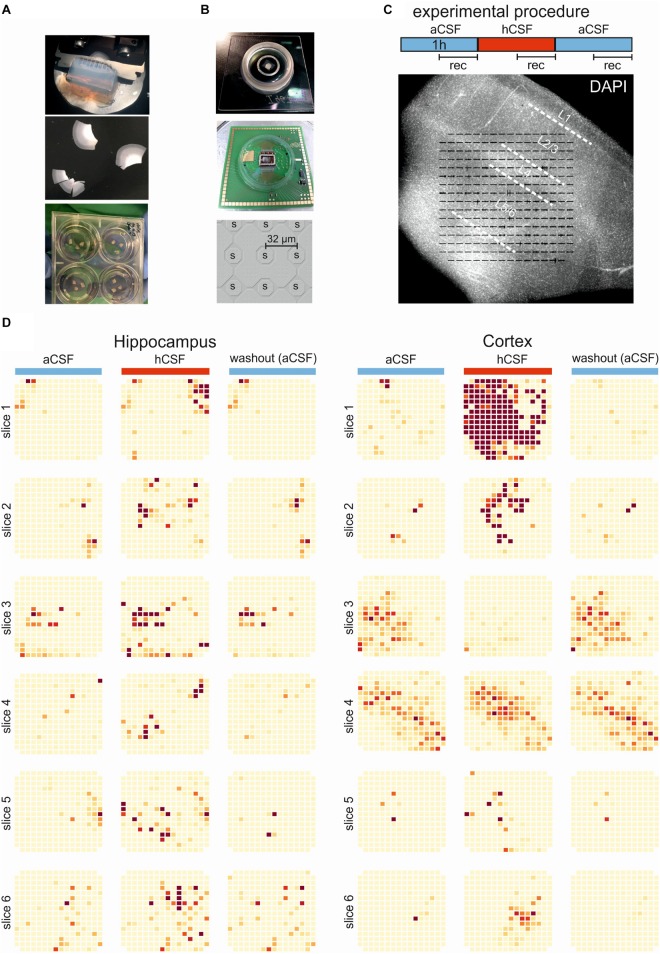
FIGURE 1.
Experimental and overview of activity. (A) The brain tissue is surgically resected en bloc and the tissue block (top) is cut into 250-μm slices (middle) using a vibratome. The slices are incubated on membrane insets in six-well plates (bottom) with hCSF as medium for up to 2 weeks. (B) Pictures of the 256-MEA chip (top), the CMOS-MEA chip (middle), and the spacing of the CMOS-MEA electrodes (bottom). (C) Experimental protocol. Slices were perfused with aCSF for an acclimation period of 30 min, followed by 60-min aCSF (blue bar), 60-min hCSF (red bar), and again 60-min aCSF (blue bar) perfusion. Recording was performed continuously for 30 min in aCSF, hCSF, and aCSF, as indicated. Underneath, a typical human slice culture is shown with all cortical layers (L1–L6) and overlay of the MEA on the slice. (D) Qualitative overview over all 12 slices recorded using 256-MEA. When hCSF was washed in, the general activity of slices increased, with new active areas emerging and with the already active areas showing a further increase in number of spikes presented here as heat maps. Each electrode is represented by a small square and darker color indicates higher activity (spike rate). Activity was normalized for each slice to the maximum spike rate per electrode in aCSF.