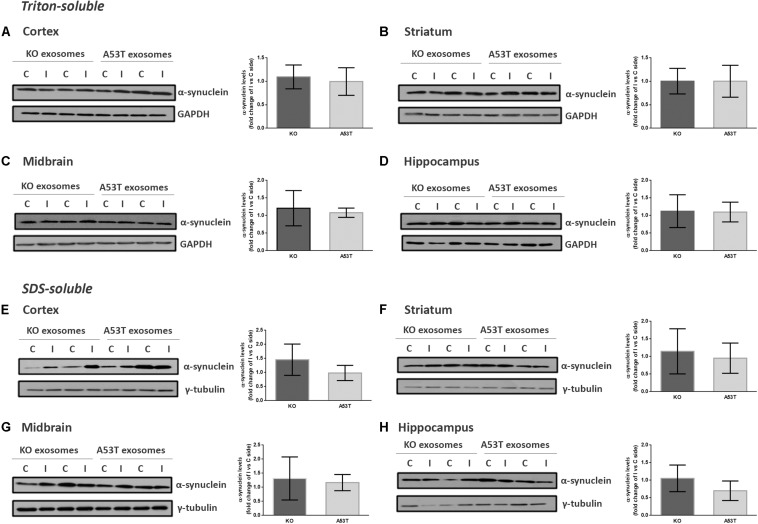
FIGURE 2.
Wild-type (wt) mice injected with KO or A53T brain exosomes display similar levels of detergent-soluble and detergent-insoluble α-syn in their brains. The cortex, striatum, midbrain, and hippocampus were isolated from exosome-injected wt mice at 150 dpi. Brain homogenates from the ipsilateral and contralateral sides were analyzed by immunoblotting using the Syn-1 antibody to α-syn. GAPDH and γ-tubulin were used as loading controls for Triton X- and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-soluble fractions, respectively. Representative (in duplicate) immunoblots from (A/E) cortex, (B/F) striatum (C/G), midbrain, and (D/H) hippocampus are depicted. Differences in the levels of α-syn in the Triton X-soluble and SDS-soluble fractions were further evaluated by densitometry quantification. The fold changes between the ipsilateral and contralateral sides in α-syn levels are shown in the graphs. No significant differences in the levels of α-syn species were detected. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of n = 4 animals/group.