Figure 1.
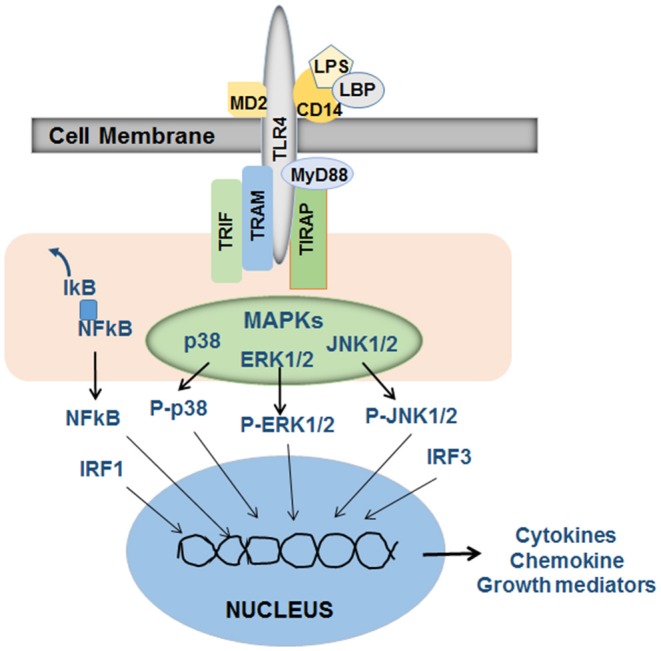
Schematic of LPS-induced signaling in inflammatory cells. LPS in association with LBP (LPS-binding protein) binds to CD14, which then stimulates TLR4 signaling. The adapter proteins MD2 (on the outer side of the cell membrane), and TRIF (TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β), TRAM (TRIF-related adaptor molecule), MyD88 and TIRAP (Toll-Interleukin 1 receptor domain containing adaptor protein) that are associated with the intracellular part of TLR4 are required for LPS-induced and TLR4-stimulated activation of intracellular signaling via NFkB, mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) p38, ERK1/2, and JNK1/2 and well as interferon-regulatory factor (IRF) 1 and 3. Translocation of these activated transcription factors to the nucleus and their subsequent binding to appropriate promoter regions on the DNA instigate transcription of a several cytokines, chemokines and growth mediators specific to a given cell type. The released mediators then act on target cells to promote pathophysiological processes. Adapted from Schwabe et al. (27), Akira et al. (28).
