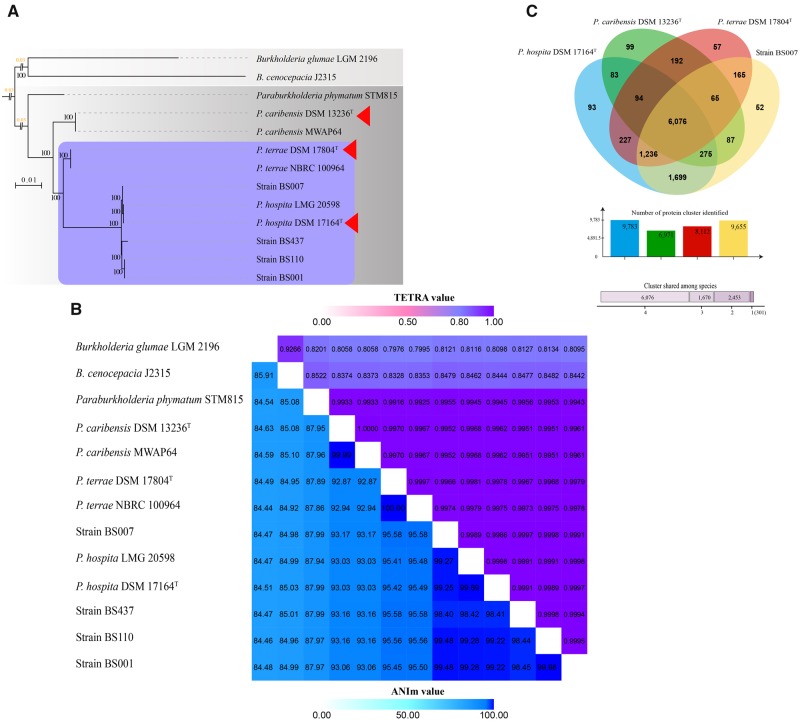
Fig. 3.
—(A) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree based multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) using seven concatenated core genes (aroE, dnaE, groeL, gyrB, mutL, recA, and rpoB). The tree was built with RAxML using amino acid substitution model PROTGAMMA, default matrix setting (Dayhoff) and algorithm (hill-climbing), with bootstrap value of 1,000 replicates. Bootstrap confidence values ≥ 70% are indicated. Purple box represents the proposed “species-cluster,” and red triangles indicate the type strains. (B) Heat maps of average nucleotide identity (ANIm) and tetranucleotide frequency (TETRA) analyses. The ANI (threshold 95–96%) and TETRA (>0.99) values were used for species circumscriptions (Richter and Rossello-Mora 2009). The ≥70% ANI coverage values were indicated. (C) Venn diagram of the orthologous clusters of proteins of P. terrae DSM 17804T, strain BS007, P. hospita DSM 17164T, and P. caribensis DSM 13236T. The number of protein clusters identified in each strain and shared protein clusters are indicated.