Figure 2.
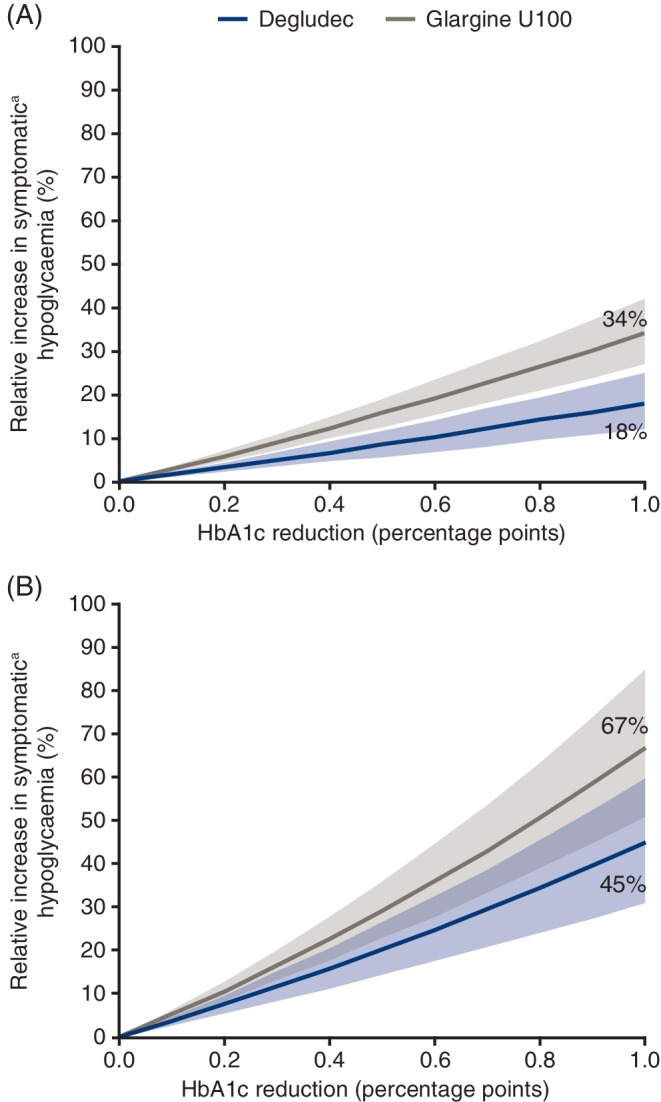
Individual patient‐level association between HbA1c reduction and the incidence of hypoglycaemia in patients with (A) type 1 diabetes or (B) type 2 diabetes, based on data from the maintenance period of the SWITCH trials.
Glargine U100, insulin glargine 100 units/mL.
Based on the full analysis set. Frequency of overall symptomatic hypoglycaemia was analyzed using Poisson regression with treatment, treatment period, sequence and time of dosing as fixed effects. The interaction between treatment and HbA1c at the end of each period was included as covariate, patient as random effect and duration of the period as offset. Data plotted are the estimated relative change in incidence of symptomatic hypoglycaemia by HbA1c reduction and 95% confidence interval.
a Symptomatic hypoglycaemia was defined as severe (requiring third‐party assistance)23 as confirmed by an event adjudication committee or blood glucose‐confirmed (<3.1 mmol/L [56 mg/dL]) accompanied by symptoms
