Figure 2.
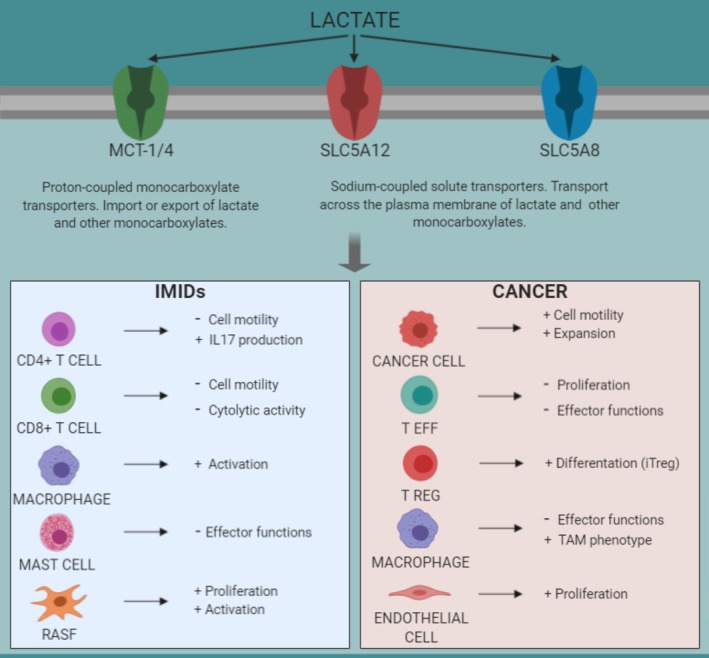
Lactate modulates immune cell functions in immune‐mediated inflammatory disorders and cancer. Immune cells “sense” high concentration of lactate which accumulates at the site of inflammation or tumor as result of accelerated metabolism of immune, stromal, or cancer cells. Lactate is taken up through specific transporters expressed on the cell membrane and modulates immune responses, including activation, differentiation, proliferation, migration, and cytokine production. These events promote the establishment of a chronic inflammatory process in IMIDs and induce tumor growth and metastatic spread in cancer
