Figure 4.
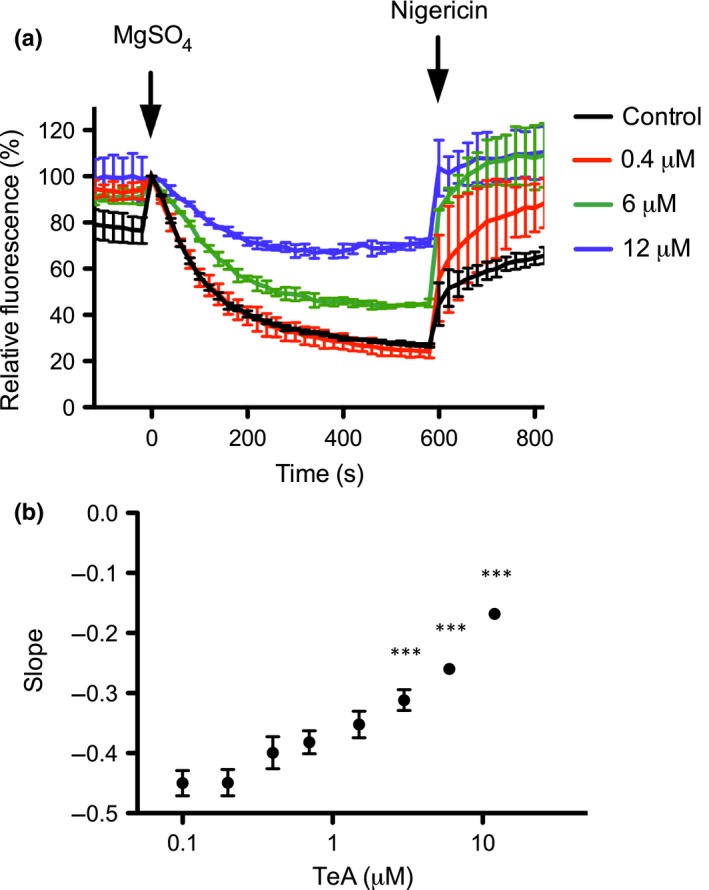
Tenuazonic acid (TeA) effect on H+ pumping of Spinacia oleracea plasma membrane (PM) vesicles. (a) Accumulation of protons in inside‐out PM vesicles of S. oleracea treated with increasing concentrations of TeA visualized and quantified using the fluorescent probe ACMA. Addition of MgSO4 initiates ATP‐stimulated proton pumping into vesicles, whereas addition of nigericin releases the trapped protons by acting as a proton ionophore. Values are means ± SEM based on two technical replicates (n = 2) and are representative of two independent PM purifications. (b) The initial slope of each curve (from t = 0 s to t = 120 s) was estimated by linear regression and plotted as a function of TeA concentration (µM). Values are means ± SEM based on two technical replicates and are representative of two independent PM fractions. Data were analyzed using one‐way ANOVA, and Dunnett's multiple comparisons test was used to calculate the difference in slopes compared to the control: ***, P < 0.001.
