Figure 4.
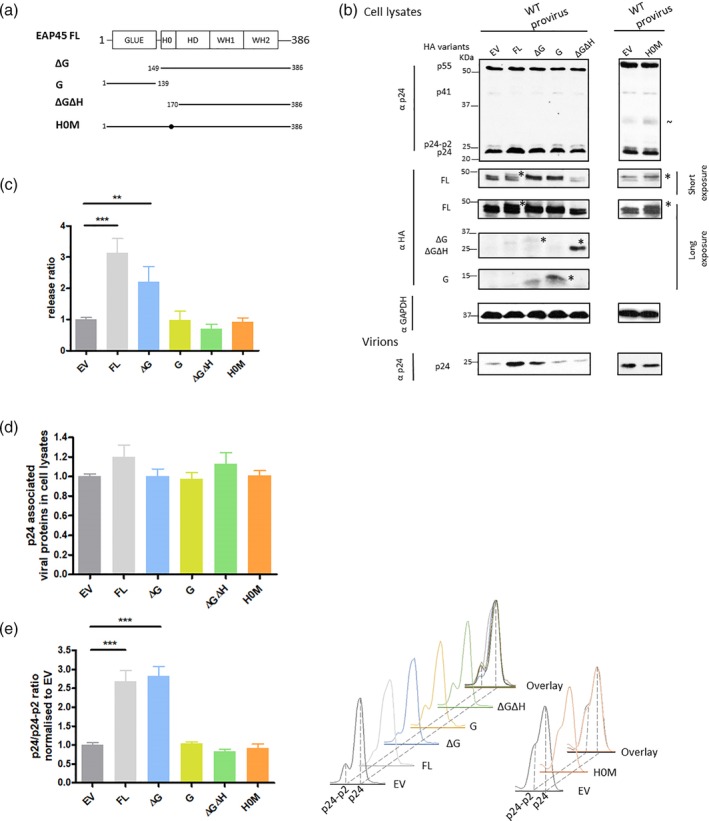
The H0 linker region in EAP45 is required for efficient rescue of HIV budding in HAP1 EAP45 KO cells. (a): Schematic diagrams of the various EAP45 variants are shown, with FL being the full‐length EAP45 expressor. Constructs are tagged with HA at the C terminus (HA tag not shown). Mutations that disrupts the putative interactions with ESCRT‐I are also introduced (H0M). The designation of each construct is shown to the left of the diagrams. (b): EAP45 KO cells were cotransfected with the WT provirus along with different EAP45 expressor mutants or empty vector (EV). Levels of proteins from cell lysates or virions were detected by immunoblotting using antibodies specific to HA, p24, or GAPDH. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Both short and long exposures are presented where necessary. (c): The virus release ratio at each condition was quantified by densitometry and normalised to that of EV as described in Figure 3. (d): Total p24‐associated viral products in the cell lysates were densitometrically quantified from Western blots and normalised to that of EV. (e): The final cleavage of Gag (p24/p24‐p2) is quantified by densitometry and normalised to that of EV. The densitometric traces of p24 and p24‐p2 for each transfection condition in (b) are shown separately or in overlay on the right. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean of five to nine replicates from at least three independent experiments
