Figure 4.
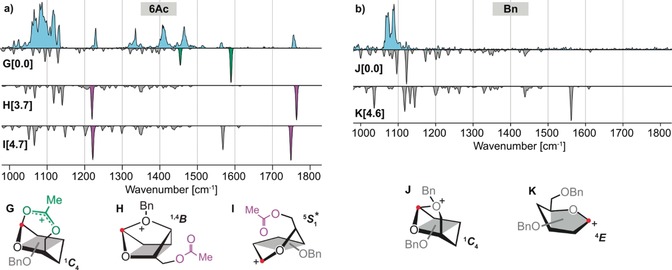
Infrared spectra of the glycosyl cations generated from a) the 6Ac and b) the Bn precursors. The blue traces show the experimental IR spectra and the gray inverted spectra are calculated spectra corresponding to the low‐energy conformers shown below in a simplified representation. Numbers in square brackets indicate free energies in kcal mol−1. The complete structures are shown in the Supporting Information. The highlighted absorption bands indicate vibrations from free acetyl groups (purple) and participating acetyl groups in dioxolenium‐type structures (green). Interestingly, both structures show non‐classical remote participation of benzyl groups at C4 or C6, leading to α‐selective oxonium intermediates. Structure I shows a heavily distorted ring pucker, closest to a 5 S 1 and 5 H 4 conformation, indicated by a star (*).
