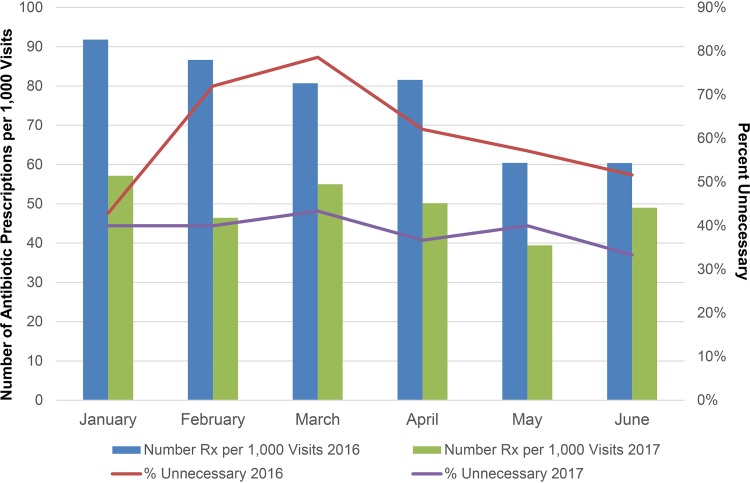
FIG 2.
Antibiotic prescriptions per 1,000 patient visits and percentages of reviewed prescriptions that were unnecessary during the baseline and intervention periods. From the baseline to the intervention period, the mean monthly antibiotic prescription rate declined from 76.9 to 49.5 prescriptions per 1,000 office visits (35.6% reduction [P < 0.001]). Among reviewed cases, unnecessary antibiotic prescribing declined from 58.8% during the baseline period to 38.9% during the intervention period (33.9% reduction [P = 0.0006]). Reviewed prescriptions are a subset of total prescriptions.