Figure 6.
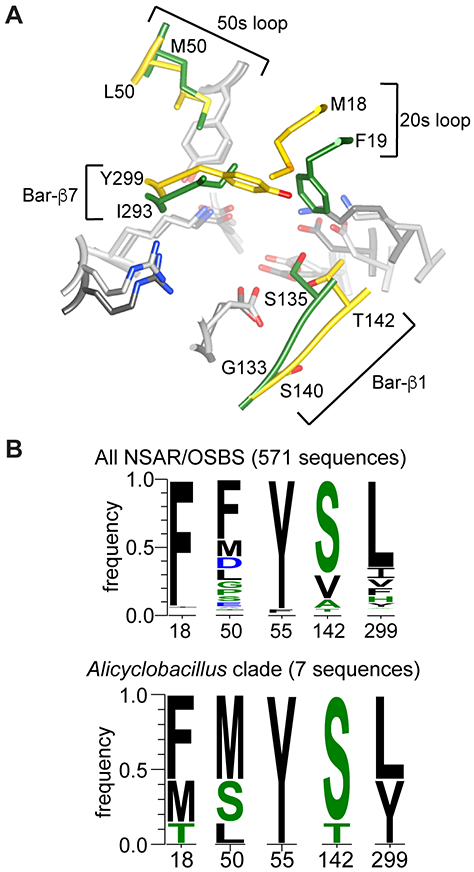
Comparison of AaOSBS to other NSAR/OSBS enzymes. A) Superposition of the active sites of AaOSBS and AmyNSAR (1SJB:B).7 Conserved amino acids are light gray (AaOSBS) or dark gray (AmyNSAR). Nonconserved residues (labeled) are gold (AaOSBS) or green (AmyNSAR). Bar-β1 and Bar-β7 are strands in the barrel domain. Alternate conformations of M18, M298, and Y299 in AaOSBS and some conserved active site residues have been omitted for clarity. B) Conservation of active site residues that differ between AaOSBS and most other NSAR/OSBS subfamily enzymes or which were predicted to affect specificity based on potential steric conflicts observed by in silico ligand docking. Height of the letters is proportional to their frequency in the data set. Positions are numbered according to AaOSBS.
