Figure 31:
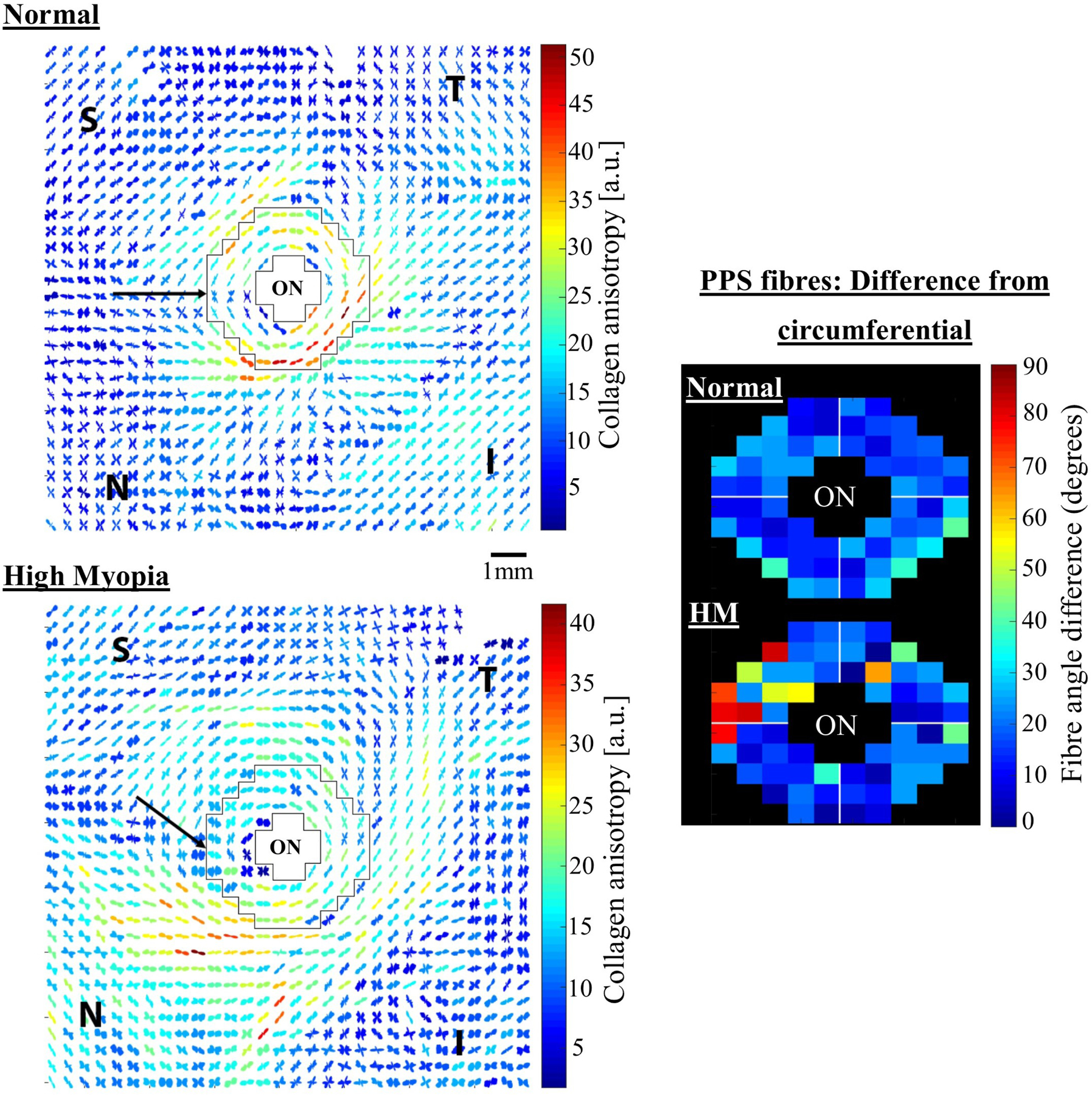
Bulk collagen microstructural changes in human high myopia. Left panel: WAXS polar vector maps of collagen orientation in (top) a normal and (bottom) a high myopia flat-mount human posterior sclera. The peripapillary sclera, bordering the optic nerve, is shown bounded in black. Note myopic alteration to collagen directions in this region. The normal sclera features a predominantly circumferential pattern, with only a slight interruption in the superior (S)-nasal (N) aspect. However the S-N interruption is far more widespread in the highly myopic eye (arrows), suggesting an unravelling of the normal structure in high myopia. Right panel: fibre displacement angle from perfect circumferential alignment in (top) average of 7 normal specimens and (bottom) the high myopia specimen. ON: optic nerve. Figure adapted from (Markov et al., 2018) with permission of Molecular Vision.
