Figure 12.
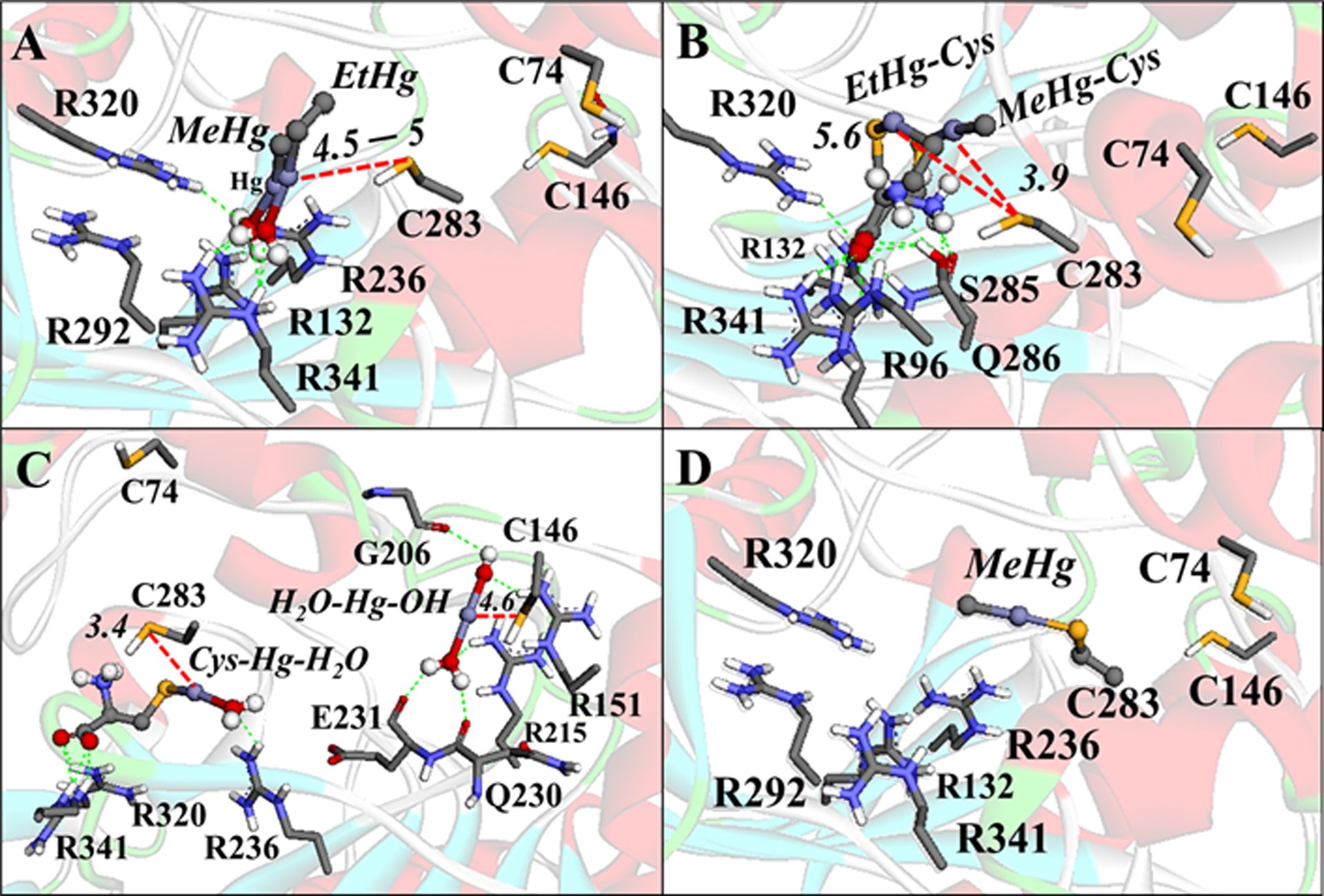
Interactions between the Hg species with CK. (A) MeHg-H2O and EtHg-H2O interactions. (B) Cys-HgMe and Cys-HgEt interactions. (C) Cys-Hg-H2O and [H2O-Hg-OH]+ interactions. (D) Simulation of the Se–Hg bond formation. H-bonds are shown in green dotted lines, Zn⋯O and Hg⋯S interactions are in red dotted lines, and the cation-π interactions are in orange lines. Only the main residues involved in the interactions are shown. The distances are in Å. The molecular blind docking simulations were carried out with the Auto Dock Vina 1.1.1 program (Trott and Olson 2010) using the human brain-type Creatine Kinase (PDB: 3DRB) (Bong et al. 2008), with the coordinates x= −58.518, y=1.229, z=5.558, and the grid box size of 64×68×50Å, and an exhaustiveness = 100. The simulation of the enzyme S−Hg conjugation was done manually in the software Avogadro 1.1.1 (Hanwell et al 2012) using the amino acid residues at 5Å of the ligands (with the Cα frozen) and geometrically optimized with the universal force field (UFF) (5000 steps).
