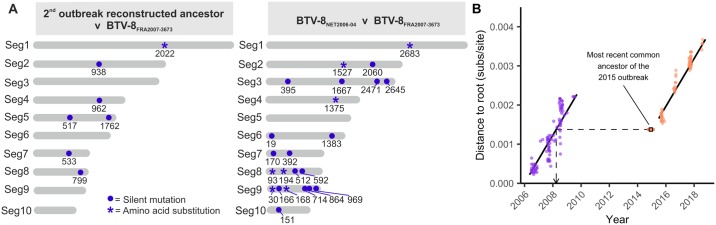
Fig 4. Lack of evolution of BTV-8 between the two European outbreaks.
(A) Graphic representation of nucleotide substitutions between the genomes of the earliest BTV-8 collected from the first European outbreak (BTV-8NET2006-04), the reconstructed ancestor of the second BTV-8 outbreak (BTV-8FRA2015), and the most similar virus to the latter sequence present in our dataset (BTV-8FRA2007-3673). Substitutions are shown as a blue circle, with numbers indicating the genomic position for each of the 10 genomic segments. Asterisks indicate those mutations inducing also an amino acid substitution. (B) Genetic divergence of 164 BTV-8 samples collected from the two European outbreaks against their sampling date (circles). The regression lines corresponding to the posterior mean estimate from the best fitting linear model for each outbreak are shown in black. Credible intervals are omitted because nonindependence of points would have made conventional estimate of standard errors invalid. When the day was unknown, the date was fixed to the 16th of the month, and when the month was unknown, the date was fixed to the midpoint of the year. The inferred age of the ancestor of the second outbreak is shown as a square, with a 95% HPD error. The dashed line indicates that the inferred ancestor of the second outbreak has a degree of divergence that is equivalent to a virus from the first outbreak circulating in 2008. Mutations can be derived from the raw sequence data deposited on GenBank under the IDs listed in S1 Table. Distances to the root can be extracted from the tree in S3 Data as MlincludingAncestor.tree, and dates are available in dateswithuncertainty.txt in S3 Data. BTV-8, bluetongue virus serotype 8; HPD, highest posterior density; Seg, virus genome segment.