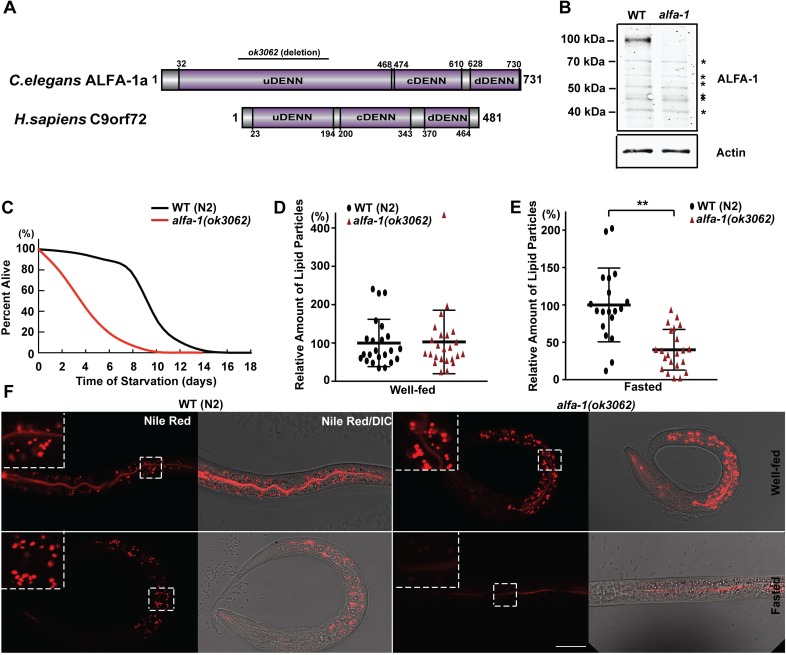
Fig 1. The C. elegans orthologue of C9orf72, alfa-1, regulates lipid metabolism at L1 diapause.
(A) The domain structure of the C. elegans ortholog of C9orf72, alfa-1. The DENN domain structure was found using the Scanprosite tool in the ExPASy Bioinformatics Resource Portal with amino acid sequences of ALFA-1, isoform a. The deletion region of the ok3062 allele is indicated by the bar. (B) Western blot analysis of ALFA-1. ALFA-1 runs at approximately 100 kDa in protein samples from wild-type animals. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands. (C) Percentage of L1 worms that survived to adulthood after starvation for the indicated time at L1. Survival of alfa-1(ok3062) after starvation was lower than that of wild-type C. elegans. (D) Quantification of the lipid particles stained with Nile Red in wild-type and alfa-1(ok3062) C. elegans under the well-fed condition. No significant difference was found in the number of Nile Red particles between N2 and alfa-1(ok3062). [p = 0.8975, n = 23 for wild-type and n = 24 for alfa-1(ok3062) C. elegans]. (E) Quantification of the lipid particles stained with Nile Red in wild-type and alfa-1(ok3062) C. elegans under the starvation condition. The number of Nile Red particles in alfa-1(ok3062) was significantly lower than that of wild-type C. elegans. [**p<0.0001, n = 19 for wild-type and n = 22 for alfa-1(ok3062) C. elegans]. (F) Representative images of Nile Red staining of L1 worms. Upper panels show the Nile Red staining of wild-type and alfa-1(ok3062) C. elegans under well-fed conditions, and the lower panels show the staining patterns of the worms under starvation conditions. Enlarged images of the boxed areas are shown in each panel. Nile Red staining was decreased in alfa-1(ok3062) when compared to wild-type C. elegans under the starvation conditions. Distribution of data points is presented with mean ± SD. Scale bar: 20 μm.