Figure 4.
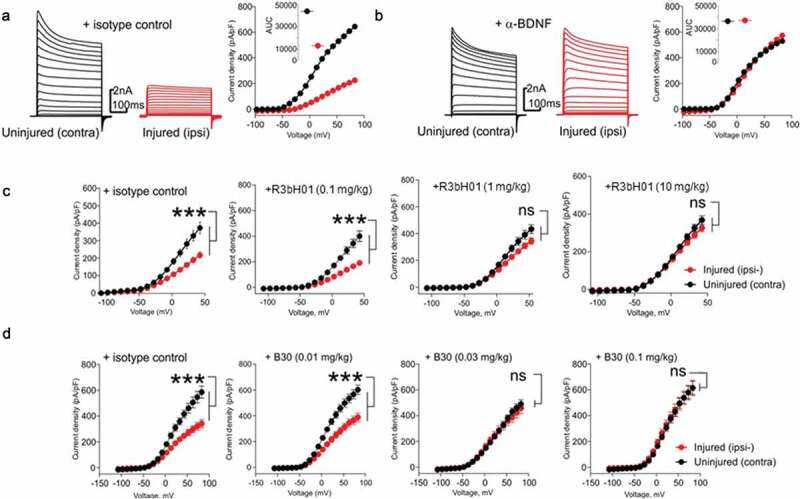
Affinity of anti-BDNF antibodies correlates to potency of neuropathy-induced Kv current suppression.
A: Representative voltage-clamp traces from acutely isolated DRG neuron from rats dosed with an isotype control antibody (0.1 mg/kg). Conductances from native Kv ion channels in an uninjured DRG neuron (black traces) are much larger than those from an injured DRG neuron (red traces). Quantification of native potassium conductance at the end of the voltage step (often termed Ik) is plotted as an I/V curve (inset shows area under the curve analysis (pA.mV.pF−1). All subsequent data is analyzed in this way with statistics being analyzed from the AUC analysis. B: Representative voltage-clamp traces from acutely isolated DRG neuron from rats dosed with a neutralizing anti-BDNF antibody (B30 0.1 mg/kg). The suppression of Kv ion channels is completely reversed by neutralization of BDNF so that the injured and uninjured conductances (and AUC values) are indistinguishable. C: R3bH01 reverses injury-induced Kv suppression in a dose-dependent manner. Voltage-activated potassium currents (as shown in A and B) are represented as a function of voltage. DRG neurons from isotype control-treated animals exhibited significantly different Kv currents as did those from animals treated with 0.1 mg/kg R3bH01. Injured DRG neurons from animals dosed with 1 or 10 mg/kg R3bH01 exhibited no significant difference in Kv currents when compared to uninjured neurons. Data are represented as mean values ± SEMs, data are analyzed using area under the curve analysis (as in A and B), unpaired t-tests were utilized to assess significance (ns = not significant, *** = p < .001). D: B30 reverses injury-induced Kv suppression in a highly potent dose-dependent manner. DRG neurons from isotype control-treated animals exhibited significantly different Kv currents as did those from animals treated with 0.01 mg/kg. Injured DRG neurons from animals dosed with 0.03 or 0.1 mg/kg B30 exhibited no significant difference in Kv currents when compared to uninjured neurons. Data are represented as mean values ± SEMs, data are analyzed using area under the curve analysis (as in A and B), unpaired t-tests were utilized to assess significance (ns = not significant, *** = p < .001).
