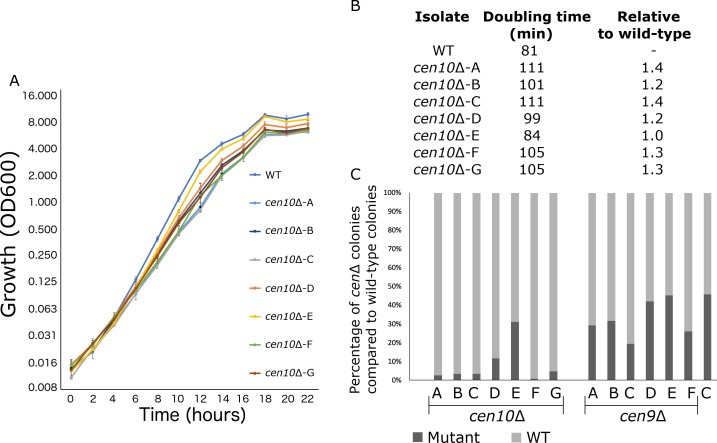
Figure 3. cen10∆ mutant strains have reduced fitness compared to the wild-type strain.
(A) Six out of seven cen10∆ mutants had a longer doubling time and slower growth than the wild-type strain. In contrast cen10∆-E grows similarly to the wild type. Error bars show standard deviation. (B) Doubling times and fold change compared to wild type are shown. (C) Competition assays with the wild type and cen9∆ and cen10∆ mutant strains. Mixed cultures (1:1) were grown overnight and plated with and without selection agents. After four days, colonies were counted and the percentage of cenΔ mutants (black) and wild type (grey) in each culture was plotted. As a control (C) a wild-type strain with a NAT marker was mixed with the wild type.