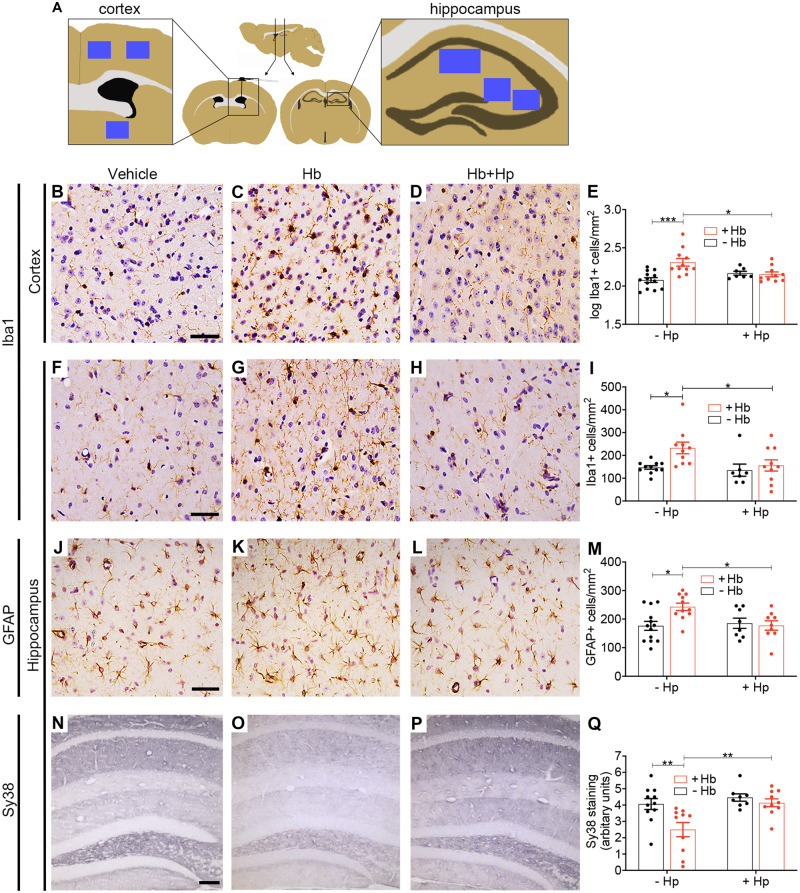
Figure 5.
In vivo animal model: histology. Hp reverses changes in immunohistochemical markers of inflammation, injury and synapse loss following prolonged intrathecal Hb exposure. (A) Sampling sites (blue squares). (B–E) Log(10) transformed counts of Iba1-positive cells in the cortex show an increase following Hb infusion, which was reduced to control levels with Hp treatment (n = 7–13 per condition). Two-way ANOVA: Hb × Hp interaction P = 0.003. (F–I) Iba1-positive cells in the hippocampal molecular region (n = 7–11 per condition). Two-way ANOVA: main effect for Hb P = 0.04. (J–M) GFAP-positive cells in the hippocampal molecular region show an increase following Hb infusion, which is reduced to control levels by Hp treatment (n = 8–13 per condition). Two-way ANOVA: Hb × Hp interaction P = 0.026. (N–Q) Sy38 (synaptophysin) staining across the hippocampal layers shows a reduction after Hb, which is reversed by Hp treatment (n = 8–11 per condition). Two-way ANOVA: Hb × Hp interaction P = 0.07. (B, F, J) Scale bar = 50 µm. (N) Scale bar = 100 µm. (E, I, M, Q) Mean ± SEM, P-values: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.