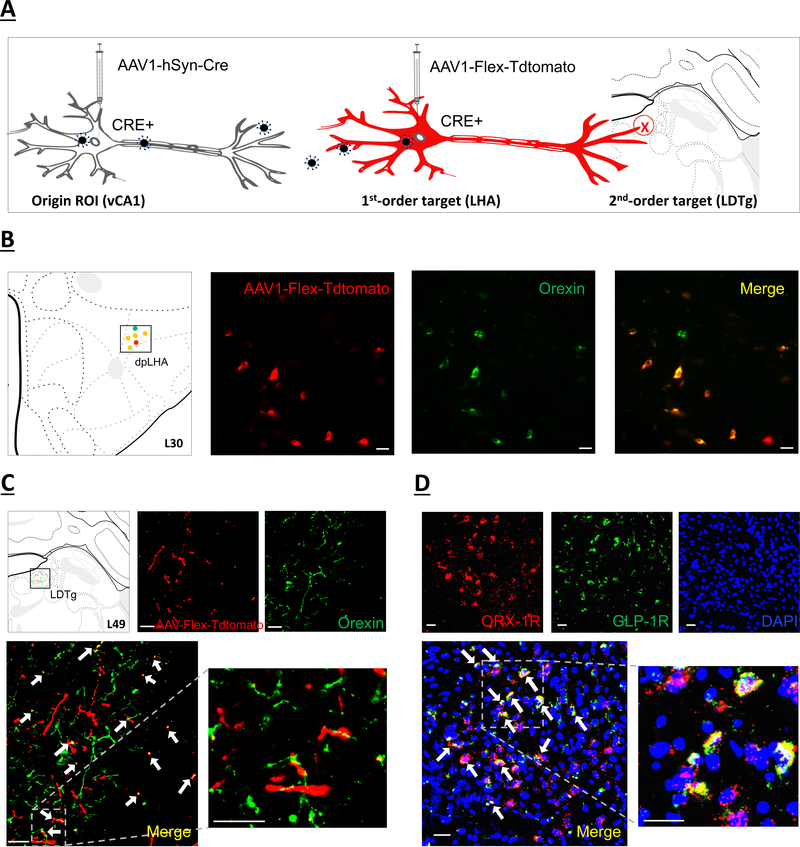
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic illustration of identifying second-order targets using a Cre-mediated multisynaptic anterograde tracing method (51). The AAV2/1-hSyn-Cre drives Cre expression in origin region of interest (ROI) infected at the injection site (left), as well as in first-order (but not second-order) neurons based on virion release from origin ROI axon terminals. The AAV-Flex-Tdtomato, a Cre-dependent anterograde tracer, will express red fluorescence in Cre+ neurons (center) and label axon terminals in second-order brain regions (right). (b) orexin immunofluorescent neurons (green) colocalize with neurons in the dpLHA that receive direct synaptic input from the vCA1 (red; AAV1-Flex-Tdtomato). Scale bar: 25μm. Left panel shows schematic representation in Swanson Atlas level 30. (c) Overlap of second-order RFP-immunoreactive axon terminal fields in the LDTg (red) of LHA neurons that receive direct input from the vCA1 and orexin axon terminal fields (green). Arrows, co-expression of RFP and orexin terminal fields. Scale bar: 25μm. Left panel shows schematic representation of terminal field overlap in Swanson Atlas level 49. (d) Representative images show ORX-1R (red) GLP-1R (green) mRNA expression in LDTg cell bodies (DAPI nuclear stain; blue) (n=3). Arrows, co-expression of GLP-1R and ORX-1R mRNA cells. Scale bar: Scale bar: 25μm. dpLHA: dorsal perifornical region of the lateral hypothalamic area; LDTg: laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; ORX-1R: orexin-1 receptor; GLP-1R: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor.